HP dc73 HP Blade Workstation Solution Planning Guide - Page 23
Network Planning
 |
View all HP dc73 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
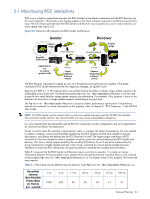
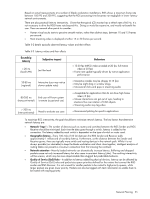
Reliability Security 5 Network Planning The HP Blade Workstation Solution changes the traditional workstation computing model by physically separating the computing and graphics resources from the user, monitor, and input devices. The computing/graphics resources and the user are connected by a standard TCP/IP network over which the RGS Sender and RGS Receiver communicate. The network design is the single most critical factor affecting operation of the HP ProLiant Blade Workstation Solution, and should focus on maximizing RGS interactivity, security and reliability (see Figure 5-1). Figure 5-1 The RGS performance triad Interactivity In a real-world network design, it is not usually possible to simultaneously maximize RGS interactivity, security and reliability-tradeoffs will be required. Your organization will need to decide on the relative importance of each of these capabilities, and then translate these decisions into network design objectives. Inherent in your network design objectives will be accommodating your capacity needs, including: • The number of blade workstations and client computers that you anticipate having on your network • The geographic locality of the blade workstations and client computers • The number of monitors connected to each client computer • The type of data generated on the blade workstations and transmitted to the client computers • The type and amount of data crossing the network not directly related to RGS (for example, market data streams, streaming video, and part files) The following sections describe how to individually maximize the RGS network characteristics-interactivity, security, and reliability. Armed with this knowledge and based on your company's priorities, you'll be better able to make the necessary network design tradeoffs. Network Planning 23