Intel BX80605X3430 Data Sheet - Page 24
Technology Enhancements of Intel, Fast Memory Access, Intel, System Memory Pre-Charge Power Down
 |
UPC - 735858210331
View all Intel BX80605X3430 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 24 highlights
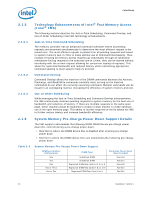
Interfaces 2.1.5 Technology Enhancements of Intel® Fast Memory Access (Intel® FMA) The following sections describe the Just-in-Time Scheduling, Command Overlap, and Out-of-Order Scheduling Intel FMA technology enhancements. 2.1.5.1 Just-in-Time Command Scheduling The memory controller has an advanced command scheduler where all pending requests are examined simultaneously to determine the most efficient request to be issued next. The most efficient request is picked from all pending requests and issued to system memory Just-in-Time to make optimal use of Command Overlapping. Thus, instead of having all memory access requests go individually through an arbitration mechanism forcing requests to be executed one at a time, they can be started without interfering with the current request allowing for concurrent issuing of requests. This allows for optimized bandwidth and reduced latency while maintaining appropriate command spacing to meet system memory protocol. 2.1.5.2 Command Overlap Command Overlap allows the insertion of the DRAM commands between the Activate, Precharge, and Read/Write commands normally used, as long as the inserted commands do not affect the currently executing command. Multiple commands can be issued in an overlapping manner, increasing the efficiency of system memory protocol. 2.1.5.3 Out-of-Order Scheduling While leveraging the Just-in-Time Scheduling and Command Overlap enhancements, the IMC continuously monitors pending requests to system memory for the best use of bandwidth and reduction of latency. If there are multiple requests to the same open page, these requests would be launched in a back to back manner to make optimum use of the open memory page. This ability to reorder requests on the fly allows the IMC to further reduce latency and increase bandwidth efficiency. 2.1.6 System Memory Pre-Charge Power Down Support Details The IMC supports and enables the following DDR3 DRAM Device pre-charge power down DLL controls during a pre-charge power down. • Slow Exit is where the DRAM device DLL is disabled after entering pre-charge power down • Fast Exit is where the DRAM device DLLs are maintained after entering pre-charge power down Table 2-3. System Memory Pre-Charge Power Down Support DIMM per Channel Configuration One Two One Two or Three One or Two DIMM Type Unbuffered DIMM Unbuffered DIMM Registered DIMM Raw Cards A, B, D, or E Registered DIMM Raw Cards A, B, D, or E Registered DIMM Raw Cards G or H Precharge Power Down Slow/Fast Exit Slow Exit Fast Exit Slow Exit Fast Exit Fast Exit 24 Datasheet, Volume 1