Intel BX80605X3430 Data Sheet - Page 28
PCI Express* Ports and Bifurcation, DMI Error Flow, Processor/PCH Compatibility Assumptions, DMI
 |
UPC - 735858210331
View all Intel BX80605X3430 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 28 highlights
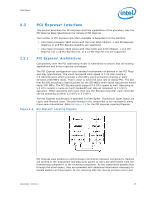
Interfaces 2.2.3 2.2.3.1 2.3 Note: 2.3.1 2.3.2 2.3.3 PCI Express* Ports and Bifurcation The PCI Express interface on the processor is a single 16 lane (x16) port that can also be configured at narrower widths. It may be bifurcated (refer to Table 6-5) and each port may train to narrower widths. The PCI Express port is designed to be compliant with the PCI Express Base Specification rev 2.0 PCI Express* Bifurcated Mode When bifurcated, the signals that had previously been assigned to lanes 15:8 of the single x16 Primary port are reassigned to lanes 7:0 of the x8 Secondary port. This assignment applies whether the lane numbering is reversed or not. The controls for the Secondary port and the associated virtual PCI-to-PCI bridge can be found in PCI Device 5. Refer to Table 6-5 for port bifurcation configuration settings and supported configurations. When the port is not bifurcated, Device 5 is hidden from the discovery mechanism used in PCI enumeration, such that configuration of the device is neither possible nor necessary. Direct Media Interface (DMI) DMI connects the processor and the PCH chip-to-chip. The DMI is similar to a four-lane PCI Express supporting up to 1 GB/s of bandwidth in each direction. Only DMI x4 configuration is supported. DMI Error Flow DMI can only generate SERR in response to errors-never SCI, SMI, MSI, PCI INT, or GPE. Any DMI related SERR activity is associated with Device 0. Processor/PCH Compatibility Assumptions The processor is compatible with the PCH and is not compatible with any previous (G)MCH or ICH products. DMI Link Down The DMI link going down is a fatal, unrecoverable error. If the DMI data link goes to data link down, after the link was up, then the DMI link hangs the system by not allowing the link to retrain to prevent data corruption. This is controlled by the PCH. Downstream transactions that had been successfully transmitted across the link prior to the link going down may be processed as normal. No completions from downstream, non-posted transactions are returned upstream over the DMI link after a link down event. 28 Datasheet, Volume 1