Lantronix XPort XChip - User Guide - Page 74
Examples, GPIO Interface, XPort., XPort User Guide
 |
View all Lantronix XPort manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 74 highlights
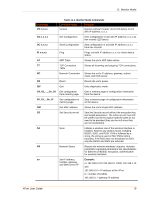
9: GPIO Interface Examples Example 1: PC sends command 10h to find out which configurable pins are available as GPIO. PC -> XPort: 10h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h XPort -> PC: 10h, 03h, 00h, 00h, 00h Command details: 10h = command 10h 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h = ignored 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h = ignored Response details: 10h = response to command 10h 03h, 00h, 00h, 00h = bits 0 and 1 are 1 →CP1 and CP2 are configured as GPIOs. bit 2 is 0 → CP3 is configured as either serial control or diagnostics. The other bits are ignored because there are only three configurable pins on the XPort. Example 2: PC sends command 1Bh to change the current states of GPIO 0 and 1. PC -> XPort: 1Bh, 01h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h XPort -> PC: 1Bh, 05h, 00h, 00h, 00h Command details: 1Bh = command 1Bh 01h, 00h, 00h, 00h = the mask that determines which GPIOs will be changed. bit 0 is 1 → GPIO0 will be changed. bit 1 is 0 → GPIO1 will remain the same. 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h = the new states bit 0 is 0 → GPIO0 will become 0. bit 1 is ignored since it is masked out. Response details: 1Bh = response to command 1Bh 05h, 00h, 00h, 00h = bit 0 is 1 → GPIO0 = 1 bit 1 is 0 → GPIO1 = 0 bit 2 is 1 → GPIO2 = 1 The other bits are ignored because there are only three configurable pins on the XPort. XPort User Guide 74