Netgear AC1450 User Manual - Page 96
Dynamic DNS, Disable Wireless Client Association, Apply
 |
View all Netgear AC1450 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 96 highlights
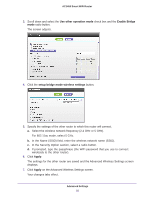
AC1450 Smart WiFi Router This IP address has to be in the same subnet as the base station, but different from the LAN IP address of the base station. 7. (Optional) Select the Disable Wireless Client Association check box to prevent wireless clients from associating with the repeater and allowing LAN client associations only. If you prefer wireless clients to be able to associate with the repeater, leave the check box cleared. 8. In the Base Station MAC Address field, enter the MAC addresses for the access point that should function as the base station. 9. Click Apply. Your changes are saved. 10. Verify connectivity across the LANs. A computer on any wireless or wired LAN segment of the router can connect to the Internet or share files and printers with any other computer or server connected to the other access point. Dynamic DNS If your Internet service provider (ISP) gave you a permanently assigned IP address, you can register a domain name and have that name linked with your IP address by public Domain Name Servers (DNS). However, if your Internet account uses a dynamically assigned IP address, you do not know the IP address in advance, and the address can change frequently. In this case, you can use a commercial Dynamic DNS service. This type of service lets you register your domain to their IP address and forwards traffic directed at your domain to your frequently changing IP address. If your ISP assigns a private WAN IP address (such as 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x), the Dynamic DNS service does not work because private addresses are not routed on the Internet. Your router contains a client that can connect to the Dynamic DNS service provided by DynDNS.org. First visit their website at http://www.dyndns.org and obtain an account and host name that you configure in the router. Then, whenever your ISP-assigned IP address changes, your router automatically contacts the Dynamic DNS service provider, logs in to your account, and registers your new IP address. If your host name is hostname, for example, you can reach your router at http://hostname.dyndns.org. Advanced Settings 96