Netgear DGND3300v2 DGND3300 User Manual - Page 26
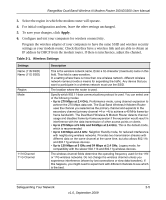
Table 2-1., Wireless Settings - slow
 |
View all Netgear DGND3300v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
RangeMax Dual Band Wireless-N Modem Router DGND3300 User Manual 3. Select the region in which the modem router will operate. 4. For initial configuration and test, leave the other settings unchanged. 5. To save your changes, click Apply. 6. Configure and test your computers for wireless connectivity. Program the wireless adapter of your computers to have the same SSID and wireless security settings as your modem router. Check that they have a wireless link and are able to obtain an IP address by DHCP from the modem router. If there is interference, adjust the channel. Table 2-1. Wireless Settings Settings Name (11N SSID) Name (11G SSID) Region Mode 11 N Channel 11 G Channel Description This is the wireless network name. Enter a 32-character (maximum) name in this field. This field is case-sensitive. In a setting where there is more than one wireless network, different wireless network names provide a means for separating the traffic. Any device that you want to participate in a wireless network must use the SSID. The location where the router is used. Specify which 802.11 data communications protocol is used. You can select one of the following modes: • Up to 270 Mbps at 2.4 GHz. Performance mode, using channel expansion to achieve the 270 Mbps data rate. The Dual Band Wireless-N Modem Router uses the channel you selected as the primary channel and expands to the secondary channel (primary channel +4 or -4) to achieve a 40 MHz frame-byframe bandwidth. The Dual Band Wireless-N Modem Router detects channel usage and disables frame-by-frame expansion if the expansion would result in interference with the data transmission of other access points or clients. • Up to 270 Mbps at 5 GHz and 54 Mbps at 2.4 GHz. This is the default mode, which is recommended. • Up to 130 Mbps at 2.4 GHz. Neighbor friendly mode, for reduced interference with neighboring wireless networks. Provides two transmission streams with different data on the same channel at the same time, but also allows 802.11b and 802.11g wireless devices. • Up to 130 Mbps at 5 GHz and 54 Mbps at 2.4 GHz. Legacy mode, for compatibility with the slower 802.11b and 802.11g wireless devices. The wireless channel fields determine the operating frequency used for the 11N or 11G wireless networks. Do not change the wireless channel unless you experience interference (shown by lost connections or slow data transfers). If this happens, you might need to experiment with different channels to see which is the best. Safeguarding Your Network 2-5 v1.0, September 2009