Netgear WNR3500Lv2 User Manual - Page 25
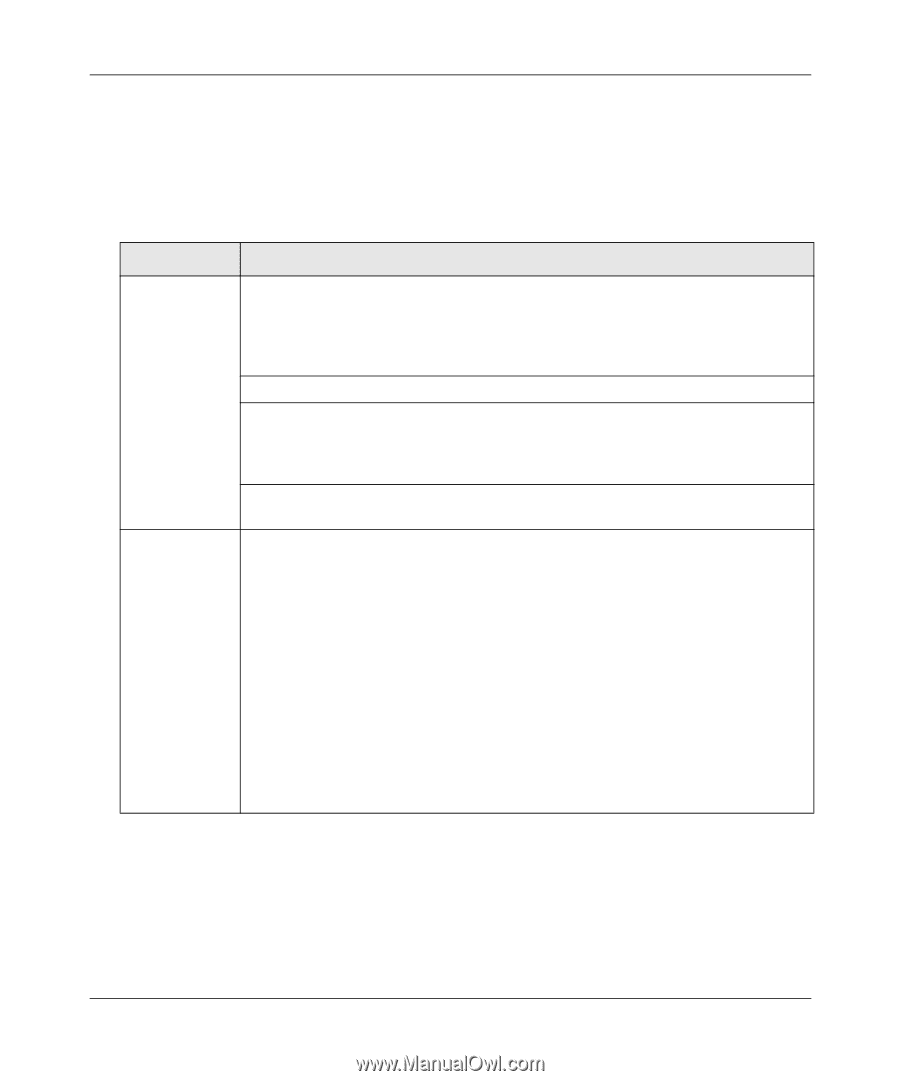
Table 2-1. Wireless Settings - slow
 |
View all Netgear WNR3500Lv2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
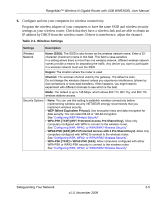
RangeMax™ Wireless-N Gigabit Router with USB WNR3500L User Manual 6. Configure and test your computers for wireless connectivity. Program the wireless adapter of your computers to have the same SSID and wireless security settings as your wireless router. Check that they have a wireless link and are able to obtain an IP address by DHCP from the wireless router. If there is interference, adjust the channel. Table 2-1. Wireless Settings Settings Description Wireless Network Name (SSID): The SSID is also known as the wireless network name. Enter a 32character (maximum) name in this field. This field is case-sensitive. In a setting where there is more than one wireless network, different wireless network names provide a means for separating the traffic. Any device you want to participate in a wireless network must use the SSID. Region: The location where the router is used. Channel: The wireless channel used by the gateway. The default is Auto. Do not change the wireless channel unless you experience interference (shown by lost connections or slow data transfers). If this happens, you might need to experiment with different channels to see which is the best. Mode: The default is up to 145 Mbps, which allows 802.11n, 802.11g, and 802.11b wireless stations access. Security Options • None. You can use this setting to establish wireless connectivity before implementing wireless security. NETGEAR strongly recommends that you implement wireless security. • WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy). Use encryption keys and data encryption for data security. You can select 64-bit or 128-bit encryption. See "Configuring WEP Wireless Security". • WPA-PSK [TKIP] (WiFi Protected Access Pre-Shared Key). Allow only computers configured with WPA to connect to the wireless router. See "Configuring WPA, WPA2, or WPA/WPA2 Wireless Security". • WPA2-PSK [AES] (Wi-Fi Protected Access with 2 Pre-Shared Keys). Allow only computers configured with WPA2 to connect to the wireless router. See "Configuring WPA, WPA2, or WPA/WPA2 Wireless Security". • WPA-PSK [TKIP] + WPA2-PSK [AES]. Allow computers configured with either WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK security to connect to the wireless router. See "Configuring WPA, WPA2, or WPA/WPA2 Wireless Security". Safeguarding Your Network 2-5 v1.0, November 2009