Yamaha TYROS Owners Manual - Page 114
Style Creator (Digital Recording
 |
View all Yamaha TYROS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 114 highlights
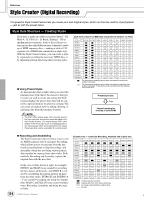
Reference Style Creator (Digital Recording) The powerful Style Creator feature lets you create your own original styles, which can then be used for style playback - just as with the preset styles. Style Data Structure - Creating Styles Each style is made up of fifteen sections (Intro I - III, Main A - D, Fill In A - D, Break, Ending I - III) as rhythm pattern variations. Each of these fifteen sections in turn has eight different parts (channels), made up of MIDI sequence data - making a total of 120 separate sets of MIDI data contained in a single style. With the Style Creator feature, you can create a style by separately recording the necessary MIDI data, or by importing pattern data from other existing styles. G Using Preset Styles As shown in the chart at right, when you select the internal preset style that is the closest to the type of style you wish to create and call up the Style Creator display, the preset style data will be copied to a special memory location for creating. You can create an original style by adding, deleting, or replacing data from this memory location. Each style contains 120 MIDI data sequences (15 Sections x 8 Parts) Section Part RHYTHM 1 RHYTHM 2 INTRO I BASS CHORD 1 CHORD 2 PAD PHRASE 1 PHRASE 2 INTRO II INTRO III MAIN A MAIN B MAIN C MAIN D FILL IN A FILL IN B FILL IN C FILL IN D BREAK ENDING I ENDING II ENDING III For these parts containing preset data, new material can be overdubbed (recorded). For these parts containing preset data, new material cannot be overdubbed (recorded). These parts can be recorded only after deleting their preset data. Preset Style data Copy Internal memory for creating a style (RAM) • The DSP1 effect settings (page 136) cannot be stored in the User style data, and as such cannot be edited in the Style Creator function. This means that any DSP1 effect settings in the Preset style (such as changing speeds of the rotary speaker effect) will be deleted from the copied Preset style data, and be unavailable for creating a style. G Recording and Assembling The Style Creator provides two basic ways to create MIDI sequence data of each part: Recording, which allows you to record parts from the keyboard (using Realtime or Step Recording), and Assembly, which lets you bring various pattern data together by copying from other styles. Both methods, Recording and Assembly, replace the original data with the new data. In the case of chart shown at right, for example, INTRO I and MAIN A are created by recording the new data to all the parts, and MAIN B is created by assembling the pattern data for all parts from the other styles. INTRO III and ENDING A - C are created by keeping and using the original data. MAIN C and FILL IN A are created via three ways: Recording, Assembly, and using the original data. 114 TYROS Owner's Manual Example style - created by Recording, Assembly and original data Section Part RHYTHM 1 RHYTHM 2 INTRO I BASS CHORD 1 CHORD 2 PAD PHRASE 1 PHRASE 2 INTRO II INTRO III MAIN A MAIN B MAIN C MAIN D FILL IN A FILL IN B FILL IN C FILL IN D BREAK ENDING I ENDING II ENDING III Creating data by recording Copying data from other styles (Assembly) No change (maintaining the original data) No data 112