Yamaha TYROS Owners Manual - Page 122
Custom Style Recording via an External Sequence Recorder, Connections, Creating the Data
 |
View all Yamaha TYROS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 122 highlights
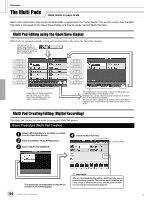
Reference Style Creator (Digital Recording) G HIGH KEY This sets the highest key (upper octave limit) of the note transposition for the chord root change. Any notes calculated to be higher than the highest key are transposed down to the next lowest octave. This setting is available only when the NTR parameter (page 121) is set to "Root Trans." Example - When the highest key is F. Root changes CM C#M Notes played C3-E3-G3 C#3-F3-G#3 FM F3-A3-C4 F#M F#2-A#2-C#3 G NOTE LIMIT This sets the note range (highest and lowest notes) for voices recorded to the style channels. By judicious setting of this range, you can ensure that the voices sound as realistic as possible - in other words, that no notes outside the natural range are sounded (e.g., high bass sounds or low piccolo sounds). The actual notes that sound are automatically shifted to the set range. Example - When the lowest note is C3 and the highest is D4. Root changes CM C#M FM Notes played E3-G3-C4 F3-G#3-C#4 F3-A3-C4 High Limit Low Limit G RTR These settings determine whether notes stop sounding or not and how they change pitch in response to chord changes. STOP PITCH SHIFT PITCH SHIFT TO ROOT RETRIGGER RETRIGGER TO ROOT The notes stop sounding. The pitch of the note will bend without a new attack to match the type of the new chord. The pitch of the note will bend without a new attack to match the root of the new chord. The note is retriggered with a new attack at a new pitch corresponding to the next chord. The note is retriggered with a new attack at the root note of the next chord. However, the octave of the new note remains the same. Custom Style Recording via an External Sequence Recorder If you have a favorite sequencer or sequence software, you can use that to create custom styles, instead of using the Style Creator on the TYROS. I Connections...• Connect the TYROS MIDI OUT to the sequencer MIDI IN, and the sequencer MIDI OUT to the TYROS MIDI IN. • Make sure that the sequencer "ECHO" function is ON, and the TYROS LOCAL ON/OFF (page 146) is turned OFF. I Creating the Data • Record all sections and parts (channels) using a CM7 (C major seventh) chord. • Record the parts on the MIDI channels listed at right, using the TYROS' internal tone generator. If the TYROS is not used during recording, make sure to use XG voices on an XG- and SFF- (Style File Format) compatible tone generator for optimum results. • Record the sections in the order listed below, with a Marker Meta-event at the top of each section. Enter the Marker Meta-events exactly as indicated in the chart on the next page (including upper/ lower case characters and spaces). • Also include an "SFF1" Marker Meta-event, "SInt" Marker Meta-event and style name Metaevent at 1|1|000 (the top of the sequence track), and the GM on Sys/Ex message (F0, 7E, 7F, 09, 01, F7). ("Timing" in the chart is based on 480 clocks per quarter note. "1|1|000" is clock "0" of the first beat of the first measure). • The data from 1|1|000 through 1|4|479 is the "Initial Setup," and 2|1|000 through the end of Ending B is the "Source Pattern." • The timing of Fill In AA and subsequent Marker Meta-events will depend on the length of each section. Part Rhythm1 Rhythm2 Bass Chord1 Chord2 Pad Phrase1 Phrase2 MIDI Ch. 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 • Explanations here assume a sequencer resolution of 480 clocks per quarter note. The actual clock values here may differ depending on your sequencer. 122 TYROS Owner's Manual 120