ZyXEL PLA450 v2 User Guide - Page 23
Getting to Know Your PLA450, 1.1 Overview, 1.1.1 Wireless LAN Application, 1.1.2 HomePlug AV
 |
View all ZyXEL PLA450 v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
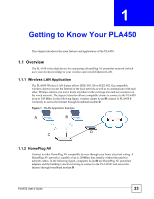
CHAPTER 1 Getting to Know Your PLA450 This chapter introduces the main features and applications of the PLA450. 1.1 Overview The PLA450 is the ideal device for connecting a HomePlug AV powerline network (which uses your electrical wiring) to your wireless and wired (Ethernet) LAN. 1.1.1 Wireless LAN Application The PLA450 Wireless LAN feature allows IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g compatible wireless clients to access the Internet or the local network as well as to communicate with each other. Wireless stations can move freely anywhere in the coverage area and use resources on the wired network. The Super G function allows compatible clients to connect to the PLA450 at up to 108 Mbps. In the following figure, wireless clients A and B connect to PLA450 C wirelessly to access the Internet through broadband modem D. Figure 1 WLAN Application Example A B D C 1.1.2 HomePlug AV Connect to other HomePlug AV compatible devices through your home electrical wiring. A HomePlug AV network is capable of up to 200Mbps data transfer without the need for network cables. In the following figure, computers A and B use HomePlug AV powerline adapters and the building's electrical wiring to connect to the PLA450 C and access the Internet through broadband modem D. PLA450 User's Guide 23