Netgear FWAG114 FWAG114 Reference Manual - Page 51
Inbound Rules Port Forwarding
 |
UPC - 606449026955
View all Netgear FWAG114 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 51 highlights
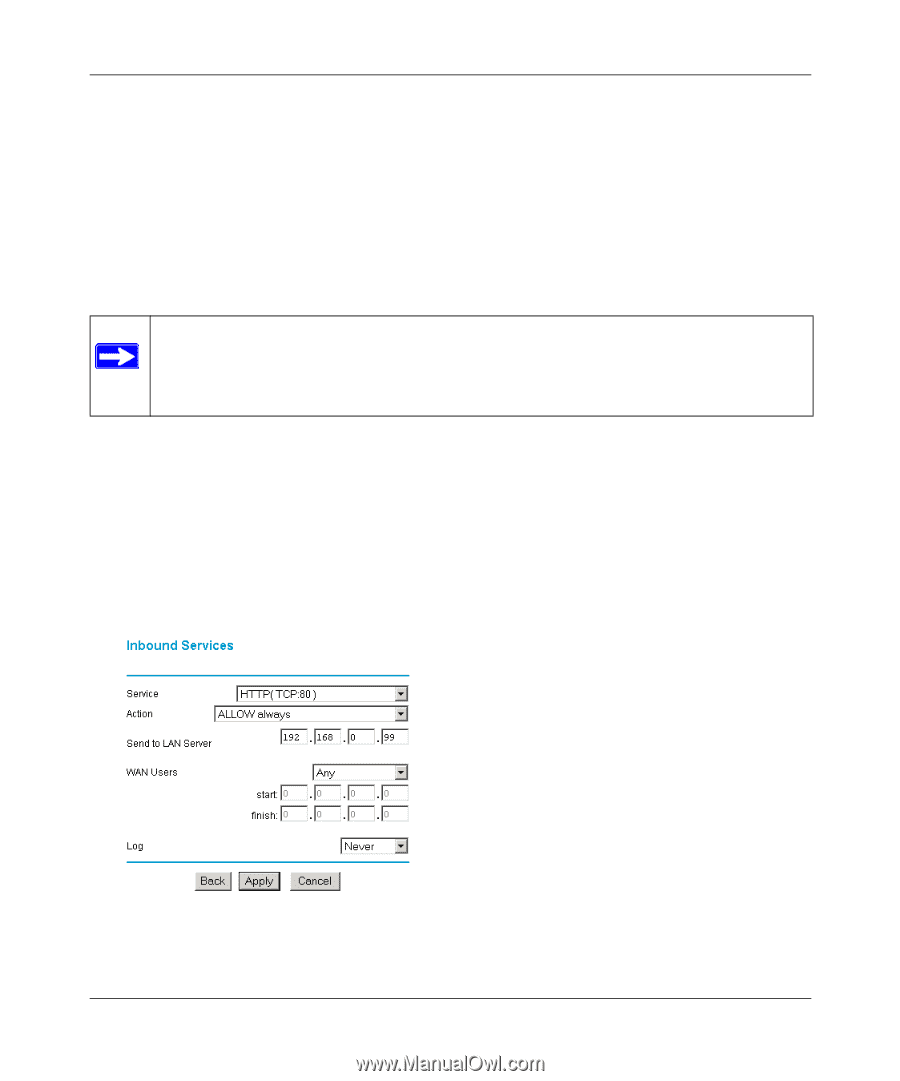
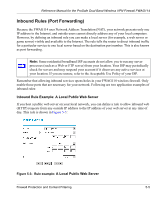
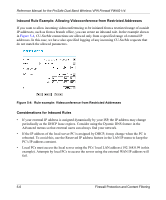
Reference Manual for the ProSafe Dual Band Wireless VPN Firewall FWAG114 Inbound Rules (Port Forwarding) Because the FWAG114 uses Network Address Translation (NAT), your network presents only one IP address to the Internet, and outside users cannot directly address any of your local computers. However, by defining an inbound rule you can make a local server (for example, a web server or game server) visible and available to the Internet. The rule tells the router to direct inbound traffic for a particular service to one local server based on the destination port number. This is also known as port forwarding. Note: Some residential broadband ISP accounts do not allow you to run any server processes (such as a Web or FTP server) from your location. Your ISP may periodically check for servers and may suspend your account if it discovers any active services at your location. If you are unsure, refer to the Acceptable Use Policy of your ISP. Remember that allowing inbound services opens holes in your FWAG114 wireless firewall. Only enable those ports that are necessary for your network. Following are two application examples of inbound rules: Inbound Rule Example: A Local Public Web Server If you host a public web server on your local network, you can define a rule to allow inbound web (HTTP) requests from any outside IP address to the IP address of your web server at any time of day. This rule is shown in Figure 5-3: Figure 5-3: Rule example: A Local Public Web Server Firewall Protection and Content Filtering 5-5