SanDisk SDCFH-004G Product Manual - Page 10
Technology Independence, Defect and Error Management, Wear Leveling, Using Erase Sector and Write
 |
UPC - 878587001044
View all SanDisk SDCFH-004G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
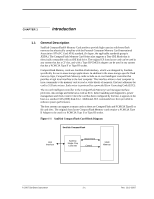
Introduction SanDisk CompactFlash Card OEM Product Manual 1.7.1 Technology Independence The 512-byte sector size of the CompactFlash Memory Card is the same as that in an IDE magnetic disk drive. To write or read a sector (or multiple sectors), the host computer software simply issues a Read or Write command to the card. This command contains the address and the number of sectors to write/read. The host software then waits for the command to complete. The host software does not get involved in the details of how the flash memory is erased, programmed or read. This is extremely important as flash devices are expected to get more and more complex in the future. Because the CompactFlash Memory Card Series uses an intelligent on-board controller, the host system software will not require changing as new flash memory evolves. In other words, systems that support CompactFlash Memory cards now, will be able to access future SanDisk cards built with new flash technology without having to update or change host software. 1.7.2 Defect and Error Management CompactFlash Memory cards contain a sophisticated defect and error management system. This system is analogous to the systems found in magnetic disk drives and in many cases offers enhancements. If necessary, the cards will rewrite data from a defective sector to a good sector. This is completely transparent to the host and does not consume any user data space. The CompactFlash Memory Card soft error rate specification is much better than the magnetic disk drive specification. In the extremely rare case a read error does occur, CompactFlash Memory cards have innovative algorithms to recover the data by using hardware on-the-fly Error Detection Code/Error Correction Code (EDC/ECC), based on a BCH algorithm. These defect and error management systems, coupled with the solid state construction, give SanDisk CompactFlash cards unparalleled reliability 1.7.3 Wear Leveling Wear Leveling is an intrinsic part of the erase pooling functionality of SanDisk CompactFlash using NAND memory. The CF WEAR LEVEL command is supported as a NOP operation to maintain backward compatibility with existing software utilities. Advanced features of dynamic and static wear-leveling, and automatic block management are used to ensure high data reliability and maximize flash life expectancy. 1.7.4 Using Erase Sector and Write Commands SanDisk CompactFlash Memory cards support the CF ERASE SECTOR and WRITE WITHOUT ERASE commands. In some applications, write operations may be faster if the addresses being written are first erased with the ERASE SECTOR command. WRITE WITHOUT ERASE behaves as a normal write command and no performance gain results from its use. 02/07, Rev. 12.0 1-4 © 2007 SanDisk Corporation