SanDisk SDCFH-004G Product Manual - Page 46
Contiguous I/O Mapped Addressing
 |
UPC - 878587001044
View all SanDisk SDCFH-004G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
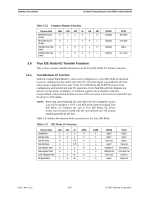
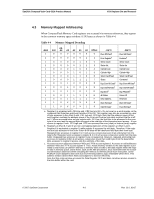
ATA Register Set and Protocol SanDisk CompactFlash Card OEM Product Manual a. Register 0 is accessed with -CE1 low and -CE2 low (and A0 = Do not care) as a word register on the combined Odd Data Bus and Even Data Bus (D15-D0). This register may also be accessed by a pair of byte accesses to the offset 0 with -CE1 low and -CE2 high. Note that the address space of this word register overlaps the address space of the Error and Feature byte-wide registers that lie at off set 1. When accessed twice as byte register with CE1 low, the first byte to be accessed is the even byte of the word and the second byte accessed is the odd byte of the equivalent word access. b. A byte access to register 0 with CE1 high and CE2 low accesses the error (read) or feature (write) register. 4.2 Contiguous I/O Mapped Addressing When the system decodes a contiguous block of I/O registers to select a CompactFlash Memory Card, the registers are accessed in the block of I/O space decoded by the system as follows: Table 4-3 Contiguous I/O Decoding -REG A3 A2 A1 A0 Offset -IORD=0 -IOWR=0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Even RD Dataa Even WR Dataa 0 0 0 0 1 1 Error Registerb Featuresb 0 0 0 1 0 2 Sector Count Sector Count 0 0 0 1 1 3 Sector No. Sector No. 0 0 1 0 0 4 Cylinder Low Cylinder Low 0 0 1 0 1 5 Cylinder High Cylinder High 0 0 1 1 0 6 Select Card/Head Select Card/Head 0 0 1 1 1 7 Status Command 0 1 0 0 0 8 Dup Even RD Datab Dup Even WR Datab 0 1 0 0 1 9 Dup Odd RD Datab Dup Odd WR Datab 0 1 1 0 1 D Dup Errorb Dup Featuresb 0 1 1 1 0 E Alt Status Device Ctl 0 1 1 1 1 F Drive Address Reserved a. Register 0 is accessed with -CE1 low and -CE2 low (and A0 = Do not care) as a word register on the combined Odd Data Bus and Even Data Bus (D15-D0). This register may also be accessed by a pair of byte accesses to the offset 0 with -CE1 low and -CE2 high. Note that the address space of this word register overlaps the address space of the Error and Feature byte-wide registers that lie at off set 1. When accessed twice as byte register with CE1 low, the first byte to be accessed is the even byte of the word and the second byte accessed is the odd byte of the equivalent word access. A byte access to register 0 with CE1 high and CE2 low accesses the error (read) or feature (write) register. b. Registers at offset 8, 9 and D are non-overlapping duplicates of the registers at offset 0 and 1. Register 8 is equivalent to register 0, while register 9 accesses the odd byte. Therefore, if the regis ters are byte accessed in the order 9 then 8 the data will be transferred odd byte then even byte. Repeated byte accesses to register 8 or 0 will access consecutive (even than odd) bytes from the data buffer. Repeated word accesses to register 8, 9 or 0 will access consecutive words from the data buffer. Repeated byte accesses to register 9 are not supported. However, repeated alternating byte accesses to registers 8 then 9 will access consecutive (even then odd) bytes from the data buffer. Byte accesses to register 9 access only the odd byte of the data. 02/07, Rev. 12.0 4-2 © 2007 SanDisk Corporation