Yamaha N12 Owners Manual - Page 29
Mastery of EQ, Boosting or cutting certain, frequency ranges, Adjusting the mid-band, center frequency
 |
UPC - 086792859866
View all Yamaha N12 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
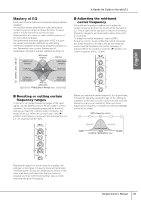
SIGNAL LEVEL (dB) English Mastery of EQ Each input channel features a three-band (high/mid/low) equalizer. An equalizer boosts (amplifies) or cuts (attenuates) certain frequency ranges to shape the tone. It can be used to modify the tone to suit the acoustic characteristics of a room, to make creative sounds, or for many other purposes. One particularly important application of EQ is to give the overall sound better definition by eliminating interference between instruments' frequency ranges in a mix. Remember: less is more. Modest use of equalization will lead to a great, natural sounding mix. LOW boost (amplify) MID boost (amplify) MID flat HIGH boost (amplify) LOW flat HIGH flat A Hands-On Guide to the n8/n12 ■ Adjusting the mid-band center frequency The mid-band equalizer enables you to adjust the center frequency at which the sound will be boosted or cut. This is useful when you want to adjust the boost/cut frequency ranges to accommodate a snare drum pitch or vocal tone. To adjust this center frequency, use the [MID] frequency control. As you rotate the control clockwise, the center frequency is raised, and as you rotate the control counter-clockwise, the center frequency is lowered. When the control is set to the (▼) position, the center frequency will be 1.0 kHz. LOW cut (attenuate) MID cut (attenuate) FREQUENCY RANGE (Hz) HIGH cut (attenuate) ■ Boosting or cutting certain frequency ranges To boost or cut certain frequency ranges of the input signal, use the [GAIN] controls. As you rotate a control clockwise, the corresponding range will be boosted, and as you rotate the control counter-clockwise, the range will be cut. When the control is set to the (▼) position, that frequency range will not be boosted or cut (i.e., its response will be "flat"). Before you adjust the center frequency, it is a good idea to boost the signal by raising the gain of the mid-band equalizer. In this way, you can easily hear and verify the frequency that you are selecting. When you finish adjusting the frequency, re-adjust the mid-band [GAIN] control to your taste. [MID] frequency control 100Hz boosted signal 1.0kHz CENTER FREQUENCY (Hz) 10.0kHz Boosting the signal too much using the equalizer will add gain to the signal, increasing noise and potentially overloading the circuitry and distorting the sound. In this case, step back and make sure that you have not boosted too much with EQ (remember, less is more!), and lower the gain if necessary. Owner's Manual 29