Adobe 22002486 Digital Signature User Guide - Page 38
Using Directory Servers to Add Trusted Identities
 |
View all Adobe 22002486 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
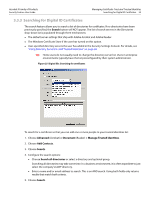
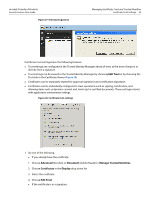
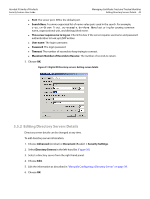
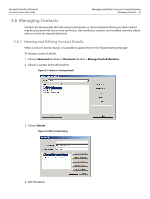
Acrobat 9 Family of Products Security Feature User Guide Managing Certificate Trust and Trusted Identities Using Certificates for Certificate Security (Encryption) 38 certificate was issued by VeriSign, you would not want to make VeriSign a trusted root unless you wanted to trust every certificate that chains up to VeriSign. Signed documents or data: Trusts the certificate for approval signatures. Tip: This setting is disabled because if the certificate is set as a trust anchor. Trust anchors are automatically trusted for approval signatures. Certified documents: Trusts the certificate for certification signatures. Dynamic content: Trusts multimedia and other dynamic content in certified documents. Selecting this option automatically adds documents that are certified with this certificate to the Trusted Documents list which is maintained by the Multimedia Trust Manager. For this reason, verify your application environment is configured correctly. For details, "Controlling Multimedia" on page 136. Embedded high privilege JavaScript: Trusts embedded scripts. Certificate settings do not override application-level settings, so even if JavaScript is enabled for a particular certificate, it may not execute unless the application's preferences allow it. This option requires that the application environment be configured correctly. For details, see "Setting JavaScript Options" on page 139. Privileged system operations (networking, printing, file access, etc.: Some operations represent a security risk more serious than others. Acrobat considers the following operations potential threats to a secure application operating environment: Internet connections, cross domain scripting, silent printing, external-object references, and FDF data injection. If this checkbox is checked, documents that are certified with this certificate will allow these actions. Tip: This feature interacts with the Enhanced Security preferences which may be set by choosing Edit > Preferences > Security (Enhanced). The application always takes the least restrictive setting when determining what is allowed. For example, if the trust level for this certificate does not allow privileged operations but the certified file resided in a privileged location, then these operations will be permitted. 3. If you need to specify a policy restriction, do so. Most users only need to set policy restrictions at the request of their administrator. "Setting Certificate Policy Restrictions" on page 39. 4. Choose OK twice. 5. Choose Close. 3.4.1 Using Certificates for Certificate Security (Encryption) You only need to specify a certificate's encryption usage if you are using certificate security. When more than one certificate is associated with the contact, you can select which one to use as the default encryption certificate. For details, see "Certificate Security" in the Document Security User Guide. 3.5 Using Directory Servers to Add Trusted Identities Businesses often use a centrally managed certificate repository such as an LDAP directory server. Directory servers are capable of returning X.509 public key certificates. These servers are searchable so that you can easily expand your list of trusted identities. Both Adobe Acrobat and Adobe Reader for Windows ship with default servers: