Canon CanoScan D1250U2F CanoScan D1250U2 ScanGear CS-U 6.3 for Win Guide - Page 60
Calibration, Canon ColorGear Color Matching, Color Channels, Color Mode, Contrast, Grayscale
 |
View all Canon CanoScan D1250U2F manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 60 highlights
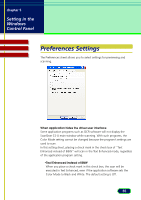
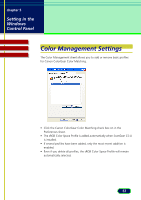
Glossary Contents Glossary Index Calibration Calibration refers to the adjustment of color processing for input and output devices on a computer, so that the colors match throughout the process. For example, calibration ensures that the color image scanned on a scanner matches the original image when it is displayed on the computer monitor, as well as printed on a color printer. Canon ColorGear Color Matching Canon's process for matching the color profile of the input device (scanner) to the color profile of the output device (monitor) to yield the most accurate color image. Color Channels The red, green, or blue components of a color image. Color images contain 8 bits per pixel each for red, green, and blue channels, therefore each pixel has 24 bits. If you are scanning a color image, you can change the brightness and contrast of the individual red, green, and blue tones in your image. Color Mode The type of scan used to scan an image, differentiated by the number of bits per pixel. ScanGear CS-U has the following Color Modes: Color, Grayscale, Text Enhanced, and Black and White. Contrast Contrast refers to the difference between the lightest light and the darkest dark in the image. A low contrast value indicates that the difference between dark shades and light shades is not very great. A high value indicates a great difference between dark and light shades. While brightness refers to the intensity of tones in an image, contrast refers to the range and number of tones in an image. 60