Dell PowerVault 56F Dell PowerVault 56F 16-Port Fibre Channel Switch Inst - Page 78
Telnet, ipAddrShow, login, logout, nsAllShow, FC4Type
 |
View all Dell PowerVault 56F manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 78 highlights
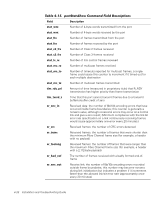
After each prompt, the current value is shown inside brackets; the user may enter one of the following actions: Press (Keeps the current value) An IP address in conventional dot (.) notation The word none Press (Cancels any changes) Press (Accepts any changes but skips remaining input) A final prompt asks whether to set IP addresses to the new values. Typing installs the new values; typing delays the changes until the next switch reboot. If the Ethernet IP address being used to Telnet to the switch is changed and the user types , then the Telnet session is closed. The ipAddrShow command displays the switch's IP addresses. The fields are described in Table 4-11. The login command allows a user to log in to the switch with a different user name and password, without first logging out. If the user is connected by way of a Telnet or log-in session, then the session is left open unlike using the logout command. This command is typically used to gain access to commands that are not allowed at the current user level. The logout command allows a user to log out from a Telnet, log in or serial port session. Telnet and log in connections are closed, the serial port returns to the prompt. The commands exit and quit are accepted as synonyms for logout, as is typed at the beginning of a line. The nsAllShow command displays the 24-bit Fibre Channel Port (FCP) IDs of all devices in all switches in the fabric. The nsAllShow command optionally takes an integer parameter, the value of the FC-PH type. The possible values for FC4Type are: 5 - FC-IP 8 - SCSI-FCP For example, nsAllShow 8 shows all SCSI-FCP nodes. If the parameter is not provided, then all Nx_Ports are displayed. 4-22 Installation and Troubleshooting Guide