HTC P3300 User Manual - Page 86
Connecting to the Internet, My ISP, My Work Network, Access point
 |
View all HTC P3300 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 86 highlights
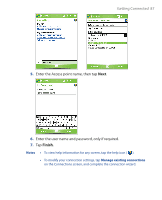
86 Getting Connected 6.1 Connecting to the Internet Your device is equipped with powerful networking functions that enable you to connect to the Internet through Wi-Fi, GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) or the mobile phone network. Connecting your device to the Internet through a private or free wireless network is your best choice since this will not incur any cost. Take note, however, that using Wi-Fi on your device will drain battery power faster. For more information about setting up a Wi-Fi connection, see "Using Wi-Fi" later in this chapter. In times when you are not within the coverage of a wireless network, you can either use GPRS or phone dial-up to connect your device to the Internet or your corporate network. Your device has two groups of connection settings: My ISP (Internet Service Provider) and My Work Network. The My ISP settings are used to connect to the Internet, while My Work Network settings can be used to connect to any private, corporate network. To set up a GPRS connection to the Internet GPRS is a non-voice value-added service that allows information to be sent and received across a mobile telephone network. You can use GPRS to connect to the Internet or to send and receive MMS on your device. You will be billed per KB (Kilobyte) by your wireless service provider when you are sending or receiving information via GPRS. If GPRS settings are not preset on your device, obtain the Access point name from your wireless service provider. Also, check with your wireless service provider if a user name and password are required. 1. Tap Start > Settings > Connections tab > Connections. 2. Under My ISP, tap Add a new modem connection. 3. On the Make New Connection screen, enter a name for the connection. 4. In the Select a modem list, select Cellular Line (GPRS), then tap Next.