HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch ACL and QoS Configuration Guide - Page 21
QoS techniques overview, Deploying QoS in a network
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
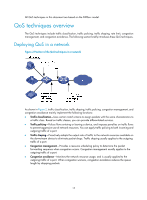
All QoS techniques in this document are based on the DiffServ model. QoS techniques overview The QoS techniques include traffic classification, traffic policing, traffic shaping, rate limit, congestion management, and congestion avoidance. The following section briefly introduces these QoS techniques. Deploying QoS in a network Figure 2 Position of the QoS techniques in a network As shown in Figure 2, traffic classification, traffic shaping, traffic policing, congestion management, and congestion avoidance mainly implement the following functions: • Traffic classification-Uses certain match criteria to assign packets with the same characteristics to a traffic class. Based on traffic classes, you can provide differentiated services. • Traffic policing-Polices flows entering or leaving a device, and imposes penalties on traffic flows to prevent aggressive use of network resources. You can apply traffic policing to both incoming and outgoing traffic of a port. • Traffic shaping-Proactively adapts the output rate of traffic to the network resources available on the downstream device to eliminate packet drops. Traffic shaping usually applies to the outgoing traffic of a port. • Congestion management-Provides a resource scheduling policy to determine the packet forwarding sequence when congestion occurs. Congestion management usually applies to the outgoing traffic of a port. • Congestion avoidance-Monitors the network resource usage, and is usually applied to the outgoing traffic of a port. When congestion worsens, congestion avoidance reduces the queue length by dropping packets. 15