HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch ACL and QoS Configuration Guide - Page 43
Rate limit, Configuring traffic policing
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 43 highlights
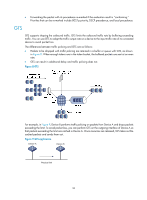
Rate limit Rate limit supports controlling the rate of inbound or outbound traffic. The outbound traffic is taken for example. The rate limit of a physical interface specifies the maximum rate for sending or receiving packets (including critical packets). Rate limit also uses token buckets for traffic control. When rate limit is configured on an interface, a token bucket handles all packets to be sent through the interface for rate limiting. If enough tokens are in the token bucket, packets can be forwarded. Otherwise, packets are put into QoS queues for congestion management. In this way, the traffic passing the physical interface is controlled. Figure 10 Rate limit implementation The token bucket mechanism limits traffic rate when accommodating bursts. It allows bursty traffic to be transmitted if enough tokens are available. If tokens are scarce, packets cannot be transmitted until efficient tokens are generated in the token bucket. It restricts the traffic rate to the rate for generating tokens. Rate limit controls the total rate of all packets on a physical interface. It is easier to use than traffic policing in controlling the total traffic rate on a physical interface. Configuring traffic policing Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Create a traffic class and enter traffic class view. Command system-view traffic classifier classifier-name [ operator { and | or } ] 3. Configure match criteria. if-match match-criteria Remarks N/A By default, no traffic class is configured. By default, no match criterion is configured. For more information about the if-match command, see ACL and QoS Command Reference. 37