HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch ACL and QoS Configuration Guide - Page 22
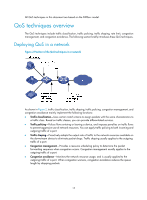
Configuring a QoS policy, Non-MQC approach, Configuration procedure diagram
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
Configuring a QoS policy You can configure QoS by using the MQC approach or non-MQC approach. Some features support both approaches, but some support only one. Non-MQC approach In the non-MQC approach, you configure QoS service parameters without using a QoS policy. For example, you can use the rate limit feature to set a rate limit on an interface without using a QoS policy. MQC approach In the modular QoS configuration (MQC) approach, you configure QoS service parameters by using QoS policies. A QoS policy defines the shaping, policing, or other QoS actions to take on different classes of traffic. It is a set of class-behavior associations. A traffic class is a set of match criteria for identifying traffic, and it uses the AND or OR operator: • If the operator is AND, a packet must match all the criteria to match the traffic class. • If the operator is OR, a packet matches the traffic class if it matches any of the criteria in the traffic class. A traffic behavior defines a set of QoS actions to take on packets, such as priority marking and redirect. By associating a traffic behavior with a traffic class in a QoS policy, you apply the specific set of QoS actions to the traffic class. Configuration procedure diagram Figure 3 shows how to configure a QoS policy. Figure 3 QoS policy configuration procedure 16