HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch ACL and QoS Configuration Guide - Page 40
Configuring traffic policing, GTS, and rate limit, Overview, Traffic evaluation and token buckets
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 40 highlights
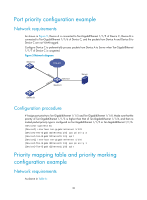
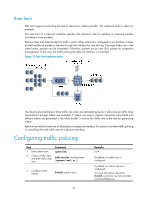
Configuring traffic policing, GTS, and rate limit Overview Traffic policing helps assign network resources (including bandwidth) and increase network performance. For example, you can configure a flow to use only the resources committed to it in a certain time range. This avoids network congestion caused by burst traffic. Traffic policing, Generic Traffic Shaping (GTS), and rate limit control the traffic rate and resource usage according to traffic specifications. You can use token buckets for evaluating traffic specifications. Traffic evaluation and token buckets Token bucket features A token bucket is analogous to a container that holds a certain number of tokens. Each token represents a certain forwarding capacity. The system puts tokens into the bucket at a constant rate. When the token bucket is full, the extra tokens cause the token bucket to overflow. Evaluating traffic with the token bucket A token bucket mechanism evaluates traffic by looking at the number of tokens in the bucket. If the number of tokens in the bucket is enough for forwarding the packets, the traffic conforms to the specification, and is called "conforming traffic." Otherwise, the traffic does not conform to the specification, and is called "excess traffic." A token bucket has the following configurable parameters: • Mean rate at which tokens are put into the bucket, which is the permitted average rate of traffic. It is usually set to the committed information rate (CIR). • Burst size or the capacity of the token bucket. It is the maximum traffic size permitted in each burst. It is usually set to the committed burst size (CBS). The set burst size must be greater than the maximum packet size. Each arriving packet is evaluated. In each evaluation, if the number of tokens in the bucket is enough, the traffic conforms to the specification and the tokens for forwarding the packet are taken away. If the number of tokens in the bucket is not enough, the traffic is excessive. Complicated evaluation You can set two token buckets, bucket C and bucket E, to evaluate traffic in a more complicated environment and achieve more policing flexibility. For example, traffic policing uses the following parameters: • CIR-Rate at which tokens are put into bucket C. It sets the average packet transmission or forwarding rate allowed by bucket C. • CBS-Size of bucket C, which specifies the transient burst of traffic that bucket C can forward. • PIR-Rate at which tokens are put into bucket E, which specifies the average packet transmission or forwarding rate allowed by bucket E. • EBS-Size of bucket E, which specifies the transient burst of traffic that bucket E can forward. 34