HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch ACL and QoS Configuration Guide - Page 50
WRR queuing,
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 50 highlights
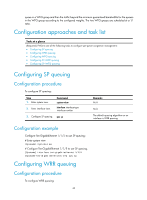
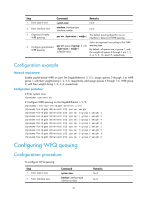
Figure 13 SP queuing In Figure 13, SP queuing classifies eight queues on a port into eight classes, numbered 7 to 0 in descending priority order. SP queuing schedules the eight queues in the descending order of priority. SP queuing sends packets in the queue with the highest priority first. When the queue with the highest priority is empty, it sends packets in the queue with the second highest priority, and so on. You can assign mission-critical packets to a high priority queue to make sure they are always served first, and common service packets to the low priority queues to be transmitted when the high priority queues are empty. The disadvantage of SP queuing is that packets in the lower priority queues cannot be transmitted if packets exist in the higher priority queues. In the worst case, lower priority traffic might never get serviced. WRR queuing WRR queuing schedules all the queues in turn to ensure every queue is served for a certain time, as shown in Figure 14. Figure 14 WRR queuing Queue 0 Weight 1 Packets to be sent through this port Queue 1 Weight 2 ...... Queue N-2 Weight N-1 Packet classification Queue N-1 Weight N Sent packets Interface Queue Sending queue scheduling 44