HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IRF Configuration Guide - Page 12
Collision handling, Failure recovery, LACP MAD
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 12 highlights
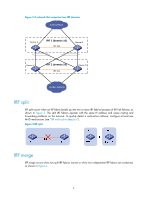
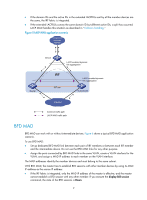
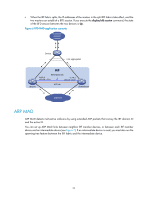
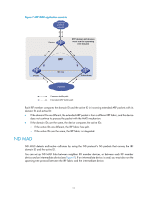
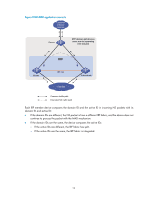
These MAD mechanisms identify each IRF fabric with a domain ID and an active ID (the member ID of the master). If multiple active IDs are detected in a domain, MAD determines that an IRF collision or split has occurred. You can use at least one of these mechanisms in an IRF fabric, depending on your network topology. IMPORTANT: LACP MAD handles collisions in a different way than BFD MAD, ARP MAD, and ND MAD. To avoid conflicts, do not use LACP MAD together with any of those mechanisms. However, you can use BFD MAD, ARP MAD, and ND MAD together. For a comparison of these MAD mechanisms, see "Configuring MAD." Collision handling MAD mechanisms remove multi-active collisions by setting one IRF fabric to the Detect state and other IRF fabrics to the Recovery state. The Detect-state IRF fabric is active. The Recovery-state IRF fabrics are inactive. Only members in the Detect-state fabric can continue to forward traffic. LACP MAD handles a multi-active collision in the following procedure: 1. Compares the number of members in each fabric. 2. Sets the fabric that has the most members to the Detect state and all other fabrics to the Recovery state. 3. If all IRF fabrics have the same number of members, compares the member IDs of their masters. 4. Sets the IRF fabric that has the lowest numbered master to the Detect state and all other fabrics to the Recovery (disabled) state. 5. Shuts down all physical network ports in the Recovery-state fabrics except their physical IRF ports and any ports you have specified with the mad exclude interface command. In contrast, BFD MAD, ARP MAD, and ND MAD do not compare the number of members in fabrics. They directly set the IRF fabric that has the lowest numbered master to the Detect state, set all other fabrics to the Recovery state, and take the same action on the network ports in Recovery-state fabrics as LACP MAD does. Failure recovery To merge two split IRF fabrics, first repair the failed IRF link and remove the IRF link failure. If the IRF fabric in Recovery state fails before the failure is recovered, repair the failed IRF fabric and the failed IRF link. If the active IRF fabric fails before the failure is recovered, first enable the inactive IRF fabric to take over the active IRF fabric and protect services from being affected. After that, recover the MAD failure. LACP MAD LACP MAD requires that every IRF member have a link with an intermediate device, and all these links form a dynamic link aggregation group, as shown in Figure 5. The intermediate device must be a device that supports extended LACP for MAD. The IRF member devices send extended LACPDUs with TLVs that convey the domain ID and the active ID of the IRF fabric. The intermediate device transparently forwards the extended LACPDUs received from one member device to all the other member switches: 8