HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IRF Configuration Guide - Page 26
Configuring IRF bridge MAC persistence
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
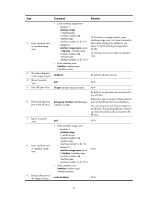
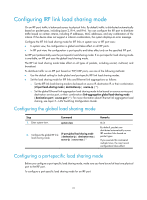
Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter IRF port view. Command system-view irf-port member-id/port-number 3. Configure the port-specific load sharing mode. irf-port load-sharing mode { destination-ip | destination-mac | source-ip | source-mac } * Remarks N/A N/A By default, packets are distributed automatically across IRF member links based on packet types. If you execute this command multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect. Configuring IRF bridge MAC persistence An IRF fabric by default uses the bridge MAC address of the master device as its bridge MAC address. Layer 2 protocols, such as LACP, use this bridge MAC address to identify the IRF fabric. On a switched LAN, the bridge MAC address must be unique. To avoid duplicate bridge MAC addresses, an IRF fabric can change its bridge MAC address automatically after its master leaves, but the change can cause temporary traffic disruption. Depending on your network condition, enable the IRF fabric to preserve or change its bridge MAC address after the master leaves. Available options include: • irf mac-address persistent timer-Bridge MAC address of the IRF fabric is retained for 6 minutes after the master leaves. If the master does not return before the timer expires, the IRF fabric uses the bridge MAC address of the new master as its bridge MAC address. This option avoids unnecessary bridge MAC address changes caused by device reboots, transient link failures, or purposeful link disconnections. • irf mac-address persistent always-Bridge MAC address of the IRF fabric does not change after the master leaves. • undo irf mac-address persistent-Bridge MAC address of the new master replaces the original one as soon as the old master leaves. IMPORTANT: • If ARP MAD or ND MAD is used, configure the undo irf mac-address persistent command to enable immediate bridge MAC address change after a master leaves. • If TRILL is configured, configure the irf mac-address persistent always command to retain the bridge MAC address even if the master has changed. • If a daisy-chained IRF fabric has aggregate links with upstream or downstream devices, configure the irf mac-address persistent always command. The setting prevents a bridge MAC change from causing transmission delay or packet loss at a master/subordinate switchover. If two IRF fabrics have the same bridge MAC address, they cannot merge. To configure the IRF bridge MAC persistence setting: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 22