HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IRF Configuration Guide - Page 15
ND MAD, ARP MAD application scenario
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
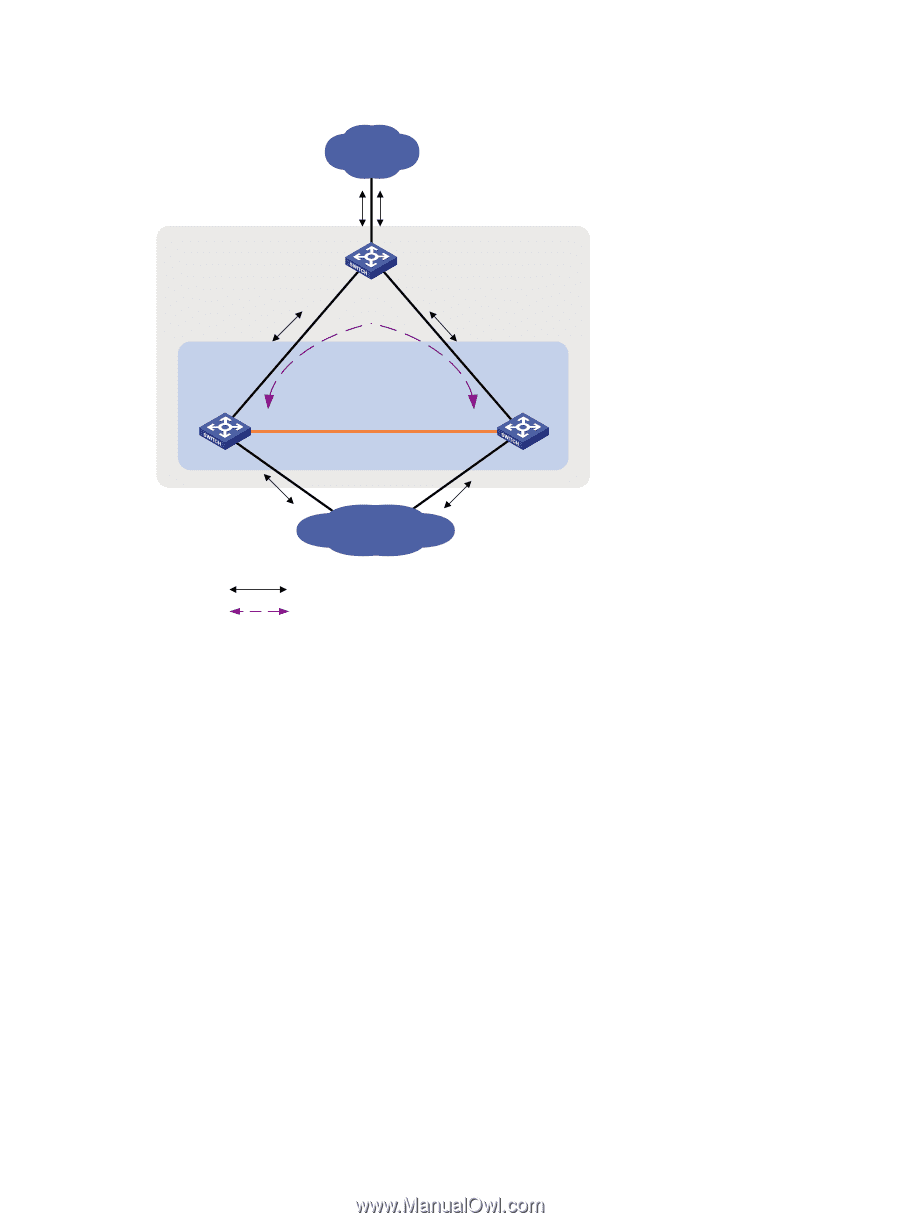
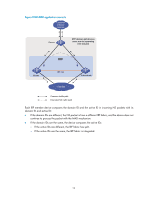
Figure 7 ARP MAD application scenario Customer premise network Device STP domain (all devices must run the spanning tree feature) IRF Master IRF link Subordinate Internet Common traffic path Extended ARP traffic path Each IRF member compares the domain ID and the active ID in incoming extended ARP packets with its domain ID and active ID: • If the domain IDs are different, the extended ARP packet is from a different IRF fabric, and the device does not continue to process the packet with the MAD mechanism. • If the domain IDs are the same, the device compares the active IDs: { If the active IDs are different, the IRF fabric has split. { If the active IDs are the same, the IRF fabric is integrated. ND MAD ND MAD detects multi-active collisions by using the ND protocol's NS packets that convey the IRF domain ID and the active ID. You can set up ND MAD links between neighbor IRF member devices, or between each IRF member device and an intermediate device (see Figure 8). If an intermediate device is used, you must also run the spanning tree protocol between the IRF fabric and the intermediate device. 11