HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IRF Configuration Guide - Page 46
ARP MAD-enabled IRF configuration example, Network requirements
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
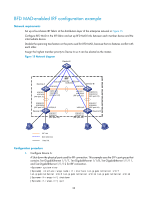
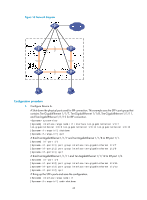
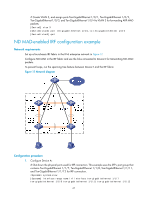
[Sysname-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/1/5] undo stp enable [Sysname-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/1/5] quit [Sysname] interface ten-gigabitethernet 2/1/5 [Sysname-Ten-GigabitEthernet2/1/5] undo stp enable [Sysname-Ten-GigabitEthernet2/1/5] quit [Sysname] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/5 [Sysname-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/5] undo stp enable [Sysname-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/5] quit [Sysname] interface ten-gigabitethernet 4/1/5 [Sysname-Ten-GigabitEthernet4/1/5] undo stp enable 6. Configure Device E as the intermediate device: CAUTION: If the intermediate device is also in an IRF fabric, assign the two IRF fabrics different domain IDs for correct split detection. False detection causes IRF split. # Create VLAN 3, and assign Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/3, and Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to VLAN 3 for forwarding BFD MAD packets. system-view [DeviceE] vlan 3 [DeviceE-vlan3] port ten-gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to ten-gigabitethernet 1/0/4 [DeviceE-vlan3] quit ARP MAD-enabled IRF configuration example Network requirements Set up a four-chassis IRF fabric in the enterprise network in Figure 16. Configure ARP MAD in the IRF fabric and use the links connected to Device E for transmitting ARP MAD packets. To prevent loops, run the spanning tree feature between Device E and the IRF fabric. 42