HP Pro 3330 HP Pro 3330 Microtower PC, HP Pro 3330 Small Form Factor PC, and H - Page 104
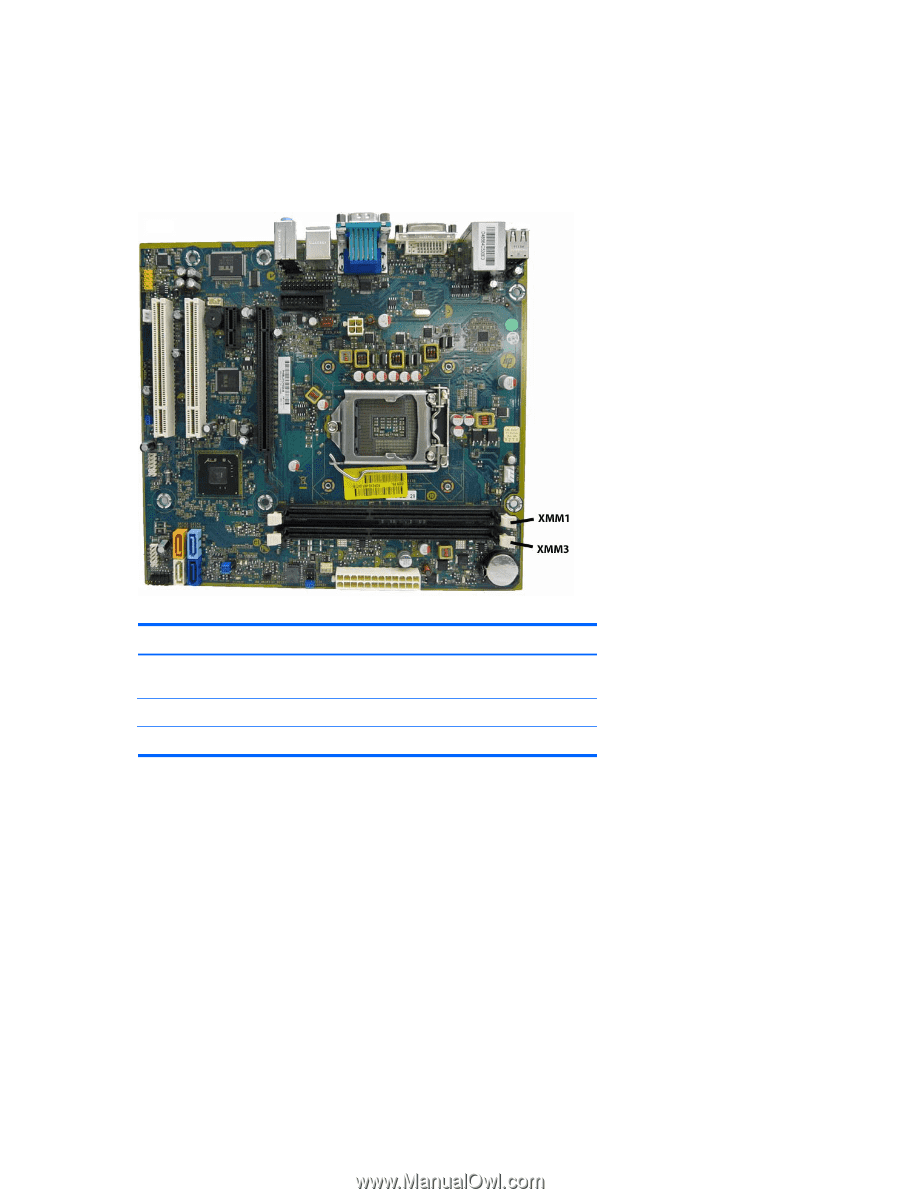
DIMM Socket Locations
 |
View all HP Pro 3330 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 104 highlights
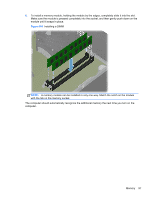
Populating DIMM Sockets There are two DIMM sockets on the system board, with one socket per channel. Populate the DIMM sockets in the following order: XMM1, then XMM3. Figure 8-5 DIMM Socket Locations Table 8-1 DIMM Socket Locations Description Socket Color XMM1 socket, Channel A (populate first) Black XMM3 socket, Channel B Black NOTE: A DIMM must occupy the XMM1 socket. Insertion Order 1 2 ● The system will operate in single channel mode if the DIMM sockets are populated in one channel only. ● The system will operate in a higher-performing dual channel mode if the total memory capacity of the DIMM in Channel A is equal to the total memory capacity of the DIMM in Channel B. The technology and device width can vary between the channels. For example, if Channel A is populated with one 2-GB DIMMs and Channel B is populated with one 2-GB DIMM, the system will operate in dual channel mode. ● The system will operate in flex mode if the total memory capacity of the DIMM in Channel A is not equal to the total memory capacity of the DIMM in Channel B. In flex mode, the channel populated with the least amount of memory describes the total amount of memory assigned to dual channel and the remainder is assigned to single channel. For optimal speed, the channels should be balanced so that the largest amount of memory is spread between the two channels. If one channel will have more memory than the other, the larger amount should be assigned to Channel A. For example, if you are populating the sockets with one 2-GB DIMM, and one 1-GB DIMMs, Channel A should be populated with the 2-GB DIMM, and Channel B should be 94 Chapter 8 Removal and Replacement Procedures - Small Form Factor (SFF) Chassis