HP ProLiant DL388e HP ProLiant DL388e Gen8 Server User Guide - Page 60
Memory subsystem architecture, Memory protection modes, Advanced ECC
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL388e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 60 highlights
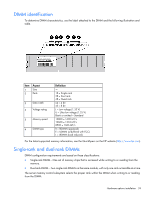
Dual-rank DIMMs provide the greatest capacity with the existing memory technology. For example, if current DRAM technology supports 2-GB single-rank DIMMs, a dual-rank DIMM would be 4 GB. Memory subsystem architecture The memory subsystem in this server is divided into channels. Each processor supports three channels, and each channel supports two DIMM slots. Channel Population order Slot number 1 A 1 D 2 2 B 3 E 4 3 C 5 F 6 DIMM slots in this server are identified by number and by letter. Letters identify the population order. Slot numbers are reported by ROM messages during boot and for error reporting. For more information, see "DIMM slot locations (on page 13)." Memory protection modes To optimize server availability, the server supports the following AMP modes: • Advanced ECC-Provides up to 4-bit error correction and enhanced performance over Lockstep memory mode. This mode is the default option for the server. • Online Spare Memory-Provides protection against failing or degraded DIMMs. Certain memory is reserved as spare, and automatic failover to spare memory occurs when the system detects a DIMM that is degrading. This enables DIMMs that have a higher probability of receiving an uncorrectable memory error (which results in system downtime) to be removed from operation. The server also can operate in independent channel mode or combined channel mode (Lockstep Memory mode). When running in Lockstep Memory mode, you gain reliability in one of two ways: • If running with UDIMMs (built with x8 DRAM devices), the system can survive a complete DRAM failure (SDDC). In independent channel mode, this failure would be an uncorrectable error. • If running with RDIMM (built with x4 DRAM devices), the system can survive the complete failure of two DRAM devices (DDDC). Running in independent mode, the server can only survive the complete failure of a single DRAM device (SDDC). Advanced Memory Protection options are configured in RBSU. If the requested AMP mode is not supported by the installed DIMM configuration, the server boots in Advanced ECC mode. For more information, see "HP ROM-Based Setup Utility (on page 103)." Advanced ECC Advanced ECC memory is the default memory protection mode for the server. Standard ECC can correct single-bit memory errors and detect multibit memory errors. When multibit errors are detected using Standard ECC, the error is signaled to the server and causes the server to halt. Advanced ECC protects the server against some multibit memory errors. Advanced ECC can correct both single-bit memory errors and 4-bit memory errors if all failed bits are on the same DRAM device on the DIMM. Hardware options installation 60