HP ProLiant DL388e HP ProLiant DL388e Gen8 Server User Guide - Page 61
Online Spare memory, Lockstep Memory mode, Memory population guidelines
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL388e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 61 highlights
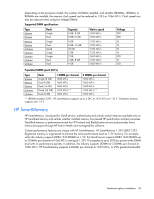
Advanced ECC provides additional protection over Standard ECC because it is possible to correct certain memory errors that would otherwise be uncorrected and result in a server failure. Using HP Advanced Memory Error Detection technology, the server provides notification when a DIMM is degrading and has a higher probability of uncorrectable memory error. Online Spare memory Online Spare memory mode provides protection against degraded DIMMs by reducing the likelihood of uncorrected memory errors. This protection is available without any operating system support. Online Spare memory protection dedicates one rank of each memory channel for use as spare memory. The remaining ranks are available for OS and application use. If correctable memory errors occur at a rate higher than a specific threshold on any of the non-spare ranks, the server automatically copies the memory contents of the degraded rank to the online spare rank. The server then deactivates the failing rank and automatically switches over to the online spare rank. Lockstep Memory mode Lockstep memory mode provides protection against multibit memory errors that occur on the same DRAM device. Lockstep memory mode can correct any single DRAM device failure on x4 and x8 DIMM types. The DIMMs in each channel must have identical HP part numbers. Lockstep memory mode uses channel 1 and channel 2. Channel 3 is not populated. Because channel 3 cannot be populated when using Lockstep memory mode, the maximum memory capacity is lower than Advanced ECC mode. Memory performance with Advanced ECC is also slightly higher. Maximum capacity Type RDIMM RDIMM LRDIMM UDIMM UDIMM Rank Single Dual Quad Single Dual Single processor 48 GB 96 GB 192 GB 12 GB 48 GB Dual processors 96 GB 192 GB 384 GB 24 GB 96 GB For the latest memory configuration information, see the QuickSpecs on the HP website (http://www.hp.com). Memory population guidelines General DIMM slot population guidelines Observe the following guidelines for all AMP modes: • Install DIMMs only if the corresponding processor is installed. • Do not mix LRDIMMs, UDIMMs, or RDIMMs. • White DIMM slots denote the first slot of a channel (1-A, 2-B, 3-C). • When two processors are installed, balance the DIMMs across the two processors. • When two processors are installed, install the DIMMs in sequential alphabetical order balanced between the two processors: P1-A, P2-A, P1-B, P2-B, P1-C, P2-C, and so forth. Hardware options installation 61