ZyXEL ES-315 User Guide - Page 87
Static Route, 14.1 Static Routing Overview, 14.2 Configuring Static Routing
 |
View all ZyXEL ES-315 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 87 highlights
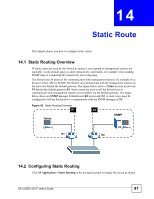
CHAPTER 14 Static Route This chapter shows you how to configure static routes. 14.1 Static Routing Overview IP static routes are used by the Switch to ensure it can respond to management stations not reachable via the default gateway and to proactively send traffic, for example when sending SNMP traps or conducting IP connectivity tests using ping. The Switch uses IP protocol for communication with management stations, for example via a browser, telnet, SSH or SNMP. The Switch can communicate with the management stations on the networks behind the default gateway. The figure below shows a Telnet session in network N1 behind the default gateway R1. Static routes are used to tell the Switch how to communicate with management stations not reachable via the default gateway. The figure below shows an SNMP manager behind router R2 in network N2. A static route must be configured to tell the Switch how to communicate with the SNMP manager in N2. Figure 42 Static Routing Overview N1 N2 Telnet SNMP R1 R2 14.2 Configuring Static Routing Click IP Application > Static Routing in the navigation panel to display the screen as shown. ES-315/ES-315-F User's Guide 87