ZyXEL G-220 User Guide - Page 107
WPA(2)-PSK Application Example, WPA(2) with RADIUS Application Example
 |
View all ZyXEL G-220 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 107 highlights
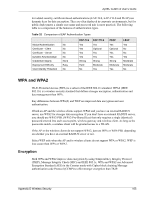
ZyXEL G-220 v2 User's Guide WPA(2)-PSK Application Example A WPA(2)s-PSK application looks as follows. 1 First enter identical passwords into the AP and all wireless clients. The Pre-Shared Key (PSK) must consist of between 8 and 63 ASCII characters or 64 hexadecimal characters (including spaces and symbols). 2 The AP checks each client's password and (only) allows it to join the network if it matches its password. 3 The AP and wireless clients use the pre-shared key to generate a common PMK. 4 The AP and wireless clients use the TKIP or AES encryption process to encrypt data exchanged between them. Figure 73 WPA-PSK Authentication WPA(2) with RADIUS Application Example You need the IP address of the RADIUS server, its port number (default is 1812), and the RADIUS shared secret. A WPA(2) application example with an external RADIUS server looks as follows. "A" is the RADIUS server. "DS" is the distribution system. 1 The AP passes the wireless client's authentication request to the RADIUS server. 2 The RADIUS server then checks the user's identification against its database and grants or denies network access accordingly. 3 The RADIUS server distributes a Pairwise Master Key (PMK) key to the AP that then sets up a key hierarchy and management system, using the pair-wise key to dynamically generate unique data encryption keys to encrypt every data packet that is wirelessly communicated between the AP and the wireless clients. Appendix D Wireless Security 107