ZyXEL G-220 User Guide - Page 37
User Authentication and Encryption, 3.2.3.1 WEP
 |
View all ZyXEL G-220 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
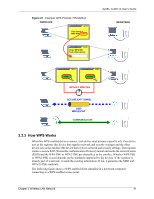
ZyXEL G-220 v2 User's Guide This type of security does not protect the information that is sent in the wireless network. Furthermore, there are ways for unauthorized wireless devices to get the MAC address of an authorized device. Then, they can use that MAC address to use the wireless network. 3.2.3 User Authentication and Encryption You can make every user log in to the wireless network before they can use it. This is called user authentication. However, every wireless client in the wireless network has to support IEEE 802.1x to do this. Wireless networks can use encryption to protect the information that is sent in the wireless network. Encryption is like a secret code. If you do not know the secret code, you cannot understand the message. 3.2.3.1 WEP 3.2.3.1.1 Data Encryption WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption scrambles all data packets transmitted between the G-220 v2 and the AP or other wireless stations to keep network communications private. Both the wireless stations and the access points must use the same WEP key for data encryption and decryption. There are two ways to create WEP keys in your G-220 v2. • Automatic WEP key generation based on a "password phrase" called a passphrase. The passphrase is case sensitive. You must use the same passphrase for all WLAN adapters with this feature in the same WLAN. For WLAN adapters without the passphrase feature, you can still take advantage of this feature by writing down the four automatically generated WEP keys from the Security Settings screen of the ZyXEL utility and entering them manually as the WEP keys in the other WLAN adapter(s). • Enter the WEP keys manually. Your G-220 v2 allows you to configure up to four 64-bit, 128-bit or 256-bit WEP keys and only one key is used as the default key at any one time. 3.2.3.1.2 Authentication Type The IEEE 802.11b/g standard describes a simple authentication method between the wireless stations and AP. Three authentication types are defined: Auto, Open System and Shared Key. • Open System mode is implemented for ease-of-use and when security is not an issue. The wireless station and the AP or peer computer do not share a secret key. Thus the wireless stations can associate with any AP or peer computer and listen to any transmitted data that is not encrypted. Chapter 3 Wireless LAN Network 37