Audiovox NAV102 Operation Manual - Page 39
Introduction, Navigation - gps navigation system
 |
View all Audiovox NAV102 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
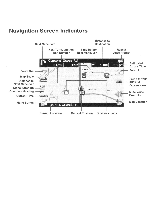
Page 39 highlights
Introduction to GPS Navigation The NAV102 is a vehicle GPS (Global Positioning System)-based navigation device which utilizes digital map data to guide you from your selected location A to location B, using location information obtained from a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). A GNSS consists of a set of satellites that transmit high-frequency radio signals containing time, direction, and distance data that can be picked up by a receiver, allowing users to pinpoint their precise locations anywhere around the globe. Navigation Satellite Receivers (GPS devices) use this transmitted information to calculate an exact location on the earth. Every point on Earth can be identified by latitude and longitude. The receiver uses the information sent by at least three satellites and determines the coordinates of the receiving device. By comparing the time the signals were transmitted from the satellites and the time they were recorded, the receiver calculates how far away each satellite is. The distance of the receiver from three or more satellites reflects its position on the surface of the planet. Using these distance measurements, the receiver might also be able to calculate speed, bearing, trip time, distance to destination, altitude, etc. The GPS position may be displayed as a point on a digital map (at least three satellites' signals must be received) and as the GPS device moves, the corresponding trace is also displayed. Please keep in mind that although the radio signals of navigation satellites will pass through clouds, glass, plastic, and other lightweight materials, satellite-navigation receivers will not work underground or in some enclosed spaces.