HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Command Refere - Page 142
Virtual Router Configuration Menu options
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 142 highlights
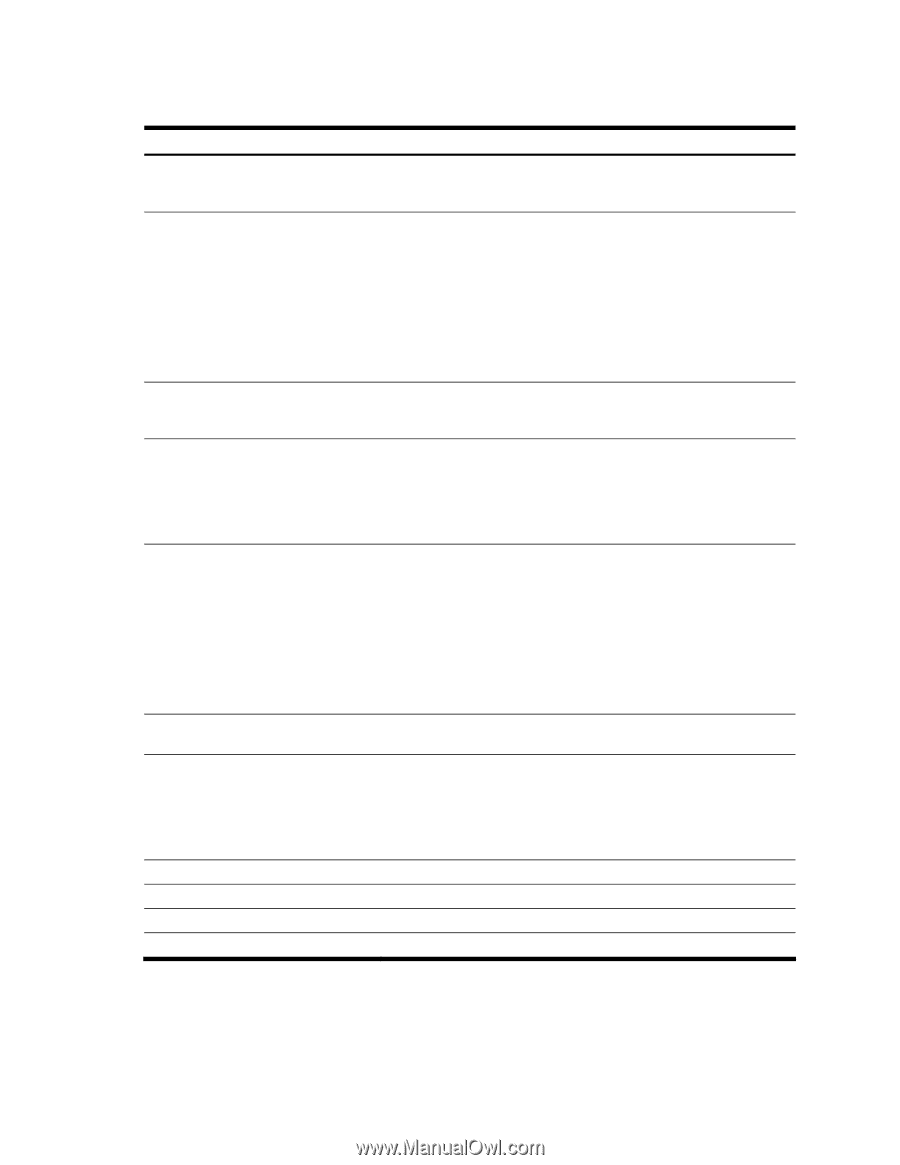
Virtual routers are disabled by default. The following table describes the Virtual Router Configuration Menu options. Table 151 Virtual Router Configuration Menu options Command track vrid addr if prio adver preem disable|enable ena dis del cur Description Displays the VRRP Priority Tracking Menu for this virtual router. Tracking is a proprietary extension to VRRP, used for modifying the standard priority system used for electing the master router. Defines the virtual router ID. This is used in conjunction with addr (below) to define a virtual router on this switch. To create a pool of VRRP-enabled routing devices which can provide redundancy to each other, each participating VRRP device must be configured with the same virtual router: one that shares the same vrid and addr combination. The vrid for standard virtual routers (where the virtual router IP address is not the same as any virtual server) can be any integer between 1 and 255. The default value is 1. All vrid values must be unique within the VLAN to which the virtual router's IP interface belongs. Defines the IP address for this virtual router using dotted decimal notation. This is used in conjunction with the vrid (above) to configure the same virtual router on each participating VRRP device. The default address is 0.0.0.0 Selects a switch IP interface. If the IP interface has the same IP address as the addr option above, this switch is considered the "owner" of the defined virtual router. An owner has a special priority of 255 (highest) and will always assume the role of master router, even if it must preempt another virtual router which has assumed master routing authority. This preemption occurs even if the preem option below is disabled. The default value is 1. Defines the election priority bias for this virtual server. This can be any integer between 1 and 254. The default value is 100. During the master router election process, the routing device with the highest virtual router priority number wins. If there is a tie, the device with the highest IP interface address wins. If this virtual router's IP address (addr) is the same as the one used by the IP interface, the priority for this virtual router will automatically be set to 255 (highest). When priority tracking is used (/cfg/l3/vrrp/track or /cfg/l3/vrrp/vr #/track), this base priority value can be modified according to a number of performance and operational criteria. Defines the time interval between VRRP master advertisements. This can be any integer between 1 and 255 seconds. The default value is 1. Enables or disables master preemption. When enabled, if this virtual router is in backup mode but has a higher priority than the current master, this virtual router will preempt the lower priority master and assume control. Note that even when preem is disabled, this virtual router will always preempt any other master if this switch is the owner (the IP interface address and virtual router addr are the same). By default, this option is enabled. Enables this virtual router. Disables this virtual router. Deletes this virtual router from the switch configuration. Displays the current configuration information for this virtual router. Configuration Menu 142