HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Command Refere - Page 16
Command line history and editing, verbose n, telnet, port], history, pushd, Ctrl-p, Backspace
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 16 highlights
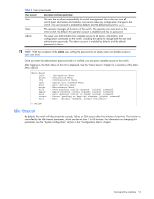
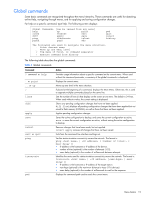
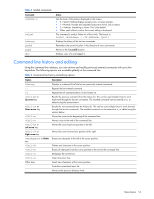
Table 4 Global commands Command verbose n telnet history pushd popd who Action Sets the level of information displayed on the screen: • 0 = Quiet: Nothing displays except errors, not even prompts. • 1 = Normal: Prompts and requested output are shown, but no menus. • 2 = Verbose: Everything is shown. This is the default. • When used without a value, the current setting is displayed. This command is used to Telnet out of the switch. The format is: telnet | [port] Displays the history of the last ten commands. Remembers the current location in the directory of menu commands. Returns to the last pushd location. Displays users who are logged in. Command line history and editing Using the command line interface, you can retrieve and modify previously entered commands with just a few keystrokes. The following options are available globally at the command line: Table 5 Command line history and editing options Option history !! !n or Up arrow key or Down arrow key or Left arrow key or Right arrow key or Delete key Other keys . .. Description Displays a numbered list of the last ten previously entered commands. Repeats the last entered command. Repeats the nth command shown on the history list. Recalls the previous command from the history list. This can be used multiple times to work backward through the last ten commands. The recalled command can be entered as is, or edited using the options below. Recalls the next command from the history list. This can be used multiple times to work forward through the last ten commands. The recalled command can be entered as is, or edited using the options below. Moves the cursor to the beginning of the command line. Moves cursor to the end of the command line. Moves the cursor back one position to the left. Moves the cursor forward one position to the right. Erases one character to the left of the cursor position. Deletes one character at the cursor position. Erases all characters from the cursor position to the end of the command line. Redisplays the current line. Clears the entire line. Inserts new characters at the cursor position. Prints the current level menu list. Moves to the previous directory level. Menu basics 16