SanDisk SDSDH-1024 Product Manual - Page 45
SD Card Protocol Description
 |
UPC - 710348911073
View all SanDisk SDSDH-1024 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 45 highlights
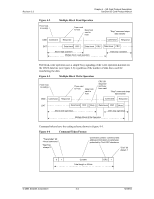
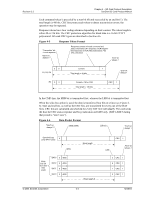
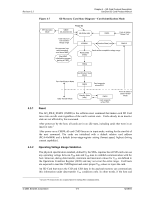
Revision 2.2 Chapter 4 - SD Card Protocol Description SanDisk SD Card Product Manual 4 SD Card Protocol Description 4.1 SD Bus Protocol Communication over the SD bus is based on command and data bit streams, which are initiated by a start bit and terminated, by a stop bit: • Command-token that starts an operation. A command is sent from the host either to a single card (addressed command) or to all connected cards (broadcast command). A command is transferred serially on the CMD line. • Response-token that is sent from an addressed card, or (synchronously) from all connected cards, to the host as an answer to a previously received command. A response is transferred serially on the CMD line. • Data-Data can be transferred from the card to the host or vice versa. Data is transferred via the data lines. Figure 4-1 "No Response" and "No Data" Operations From host to card(s) From host to card From card to host CMD DAT Command Operation (no response) Command Response Operation (no data) Card addressing is implemented using a session address that is assigned to the card during the initialization phase. The basic transaction on the SD bus is the command/response transaction (see Figure 4-1). This type of bus transaction transfers their information directly within the command or response structure. In addition, some operations have a data token. Data transfers to and from the SD Card are done in blocks. CRC bits always follow data blocks. Single and multiple block operations are defined. Note that the Multiple Block Operation mode is better for faster write operation. A multiple block transmission is terminated when a stop command follows on the CMD line. The host can configure a data transfer to use single or multiple data lines (provided the card supports this feature). © 2004 SanDisk Corporation 4-1 12/08/04