SanDisk SDSDH-1024 Product Manual - Page 5
Introduction
 |
UPC - 710348911073
View all SanDisk SDSDH-1024 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
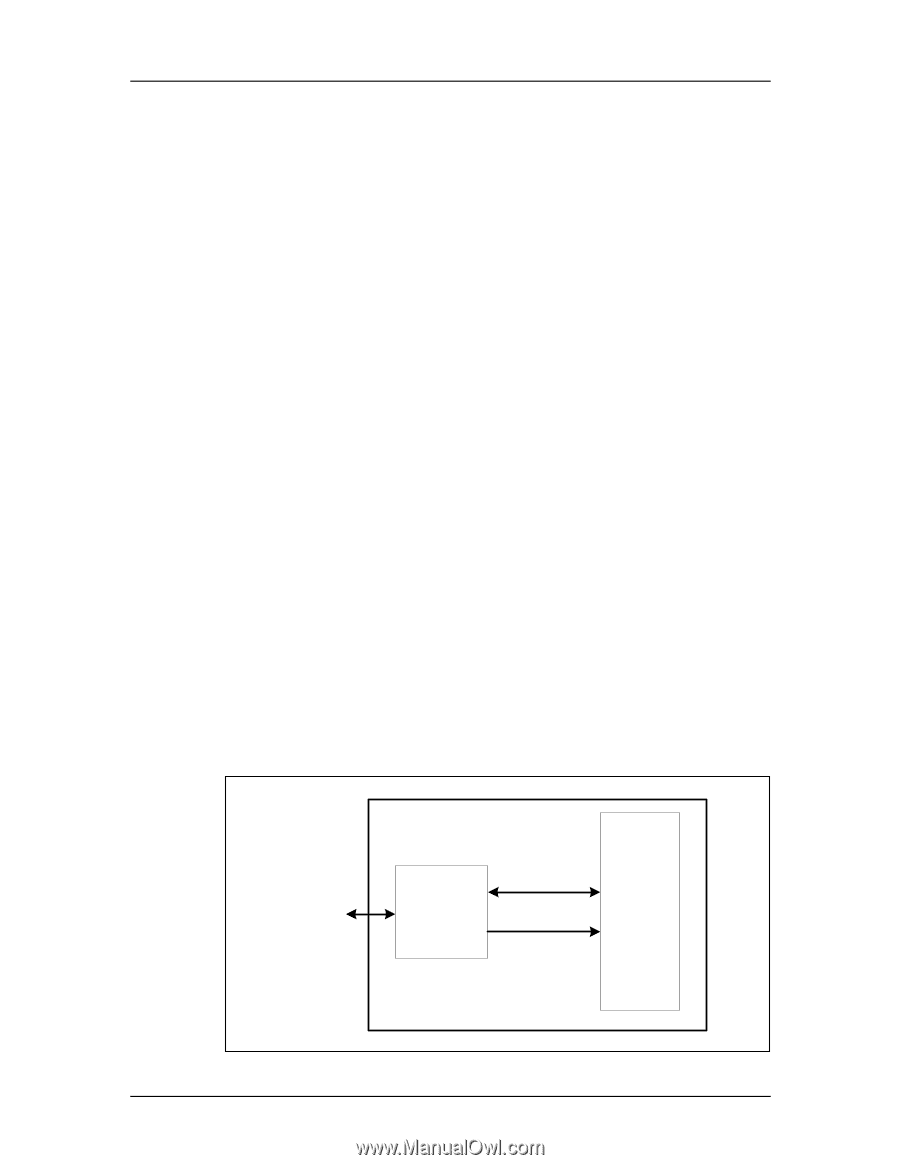
Revision 2.2 Chapter 1 - Introduction SanDisk SD Card Product Manual 1 Introduction 1.1 General Description The SanDisk Secure Digital (SD) Card is a flash-based memory card specifically designed to meet the security, capacity, performance and environmental requirements inherent in next generation mobile phones and consumer electronic devices. The SanDisk SD Card includes a copyright protection mechanism that complies with the security of the SDMI standard, and is faster and capable of higher memory capacity. The SD Card security system uses mutual authentication and a "new cipher algorithm" to protect against illegal usage of the card content. Unsecured access to the user's own content is also available. The physical form factor: pin assignment and data transfer protocol, with some additions, are forward compatible with the SD Card. SanDisk SD Card communication is based on an advanced nine-pin interface (clock, command, 4xData and 3xPower lines) designed to operate in a low voltage range. The communication protocol is defined as part of this specification. The SD Card host interface supports regular MultiMediaCard operation as well. In other words, MultiMediaCard forward compatibility was kept. The main difference between the SD Card and MultiMediaCard is the initialization process. Matsushita Electric Company (MEI), Toshiba Corporation, and SanDisk Corporation defined the SD Card Specification originally. Currently, the Secure Digital Association (SDA) controls the specifications. The SanDisk SD Card was designed to be compatible with the SD Card Physical Specification. The SD Card Interface allows for easy integration into any design, regardless of microprocessor used. For compatibility with existing controllers, the SanDisk SD Card offers, in addition to the SD Card Interface, an alternate communication protocol based on the SPI standard. Currently, the SanDisk SD Card provides up to 1024 million bytes of memory using flash memory chips, which were designed especially for use in mass storage applications. In addition to the mass storage specific flash memory chip, the SD Card includes an on-card intelligent controller which manages interface protocols, security algorithms for copyright protection, data storage and retrieval, as well as Error Correction Code (ECC) algorithms, defect handling and diagnostics, power management and clock control. Figure 1-1 SanDisk SD Card Block Diagram SD Bus/SPI Bus Interface SanDisk Single Chip Controller Data In/Out Control Flash Modules © 2004 SanDisk Corporation SanDisk SD Card 1-1 12/08/04