TP-Link TL-SG3216 TL-SG3216 V1 User Guide - Page 119
P Priority, 1.4 DSCP Priority
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG3216 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 119 highlights
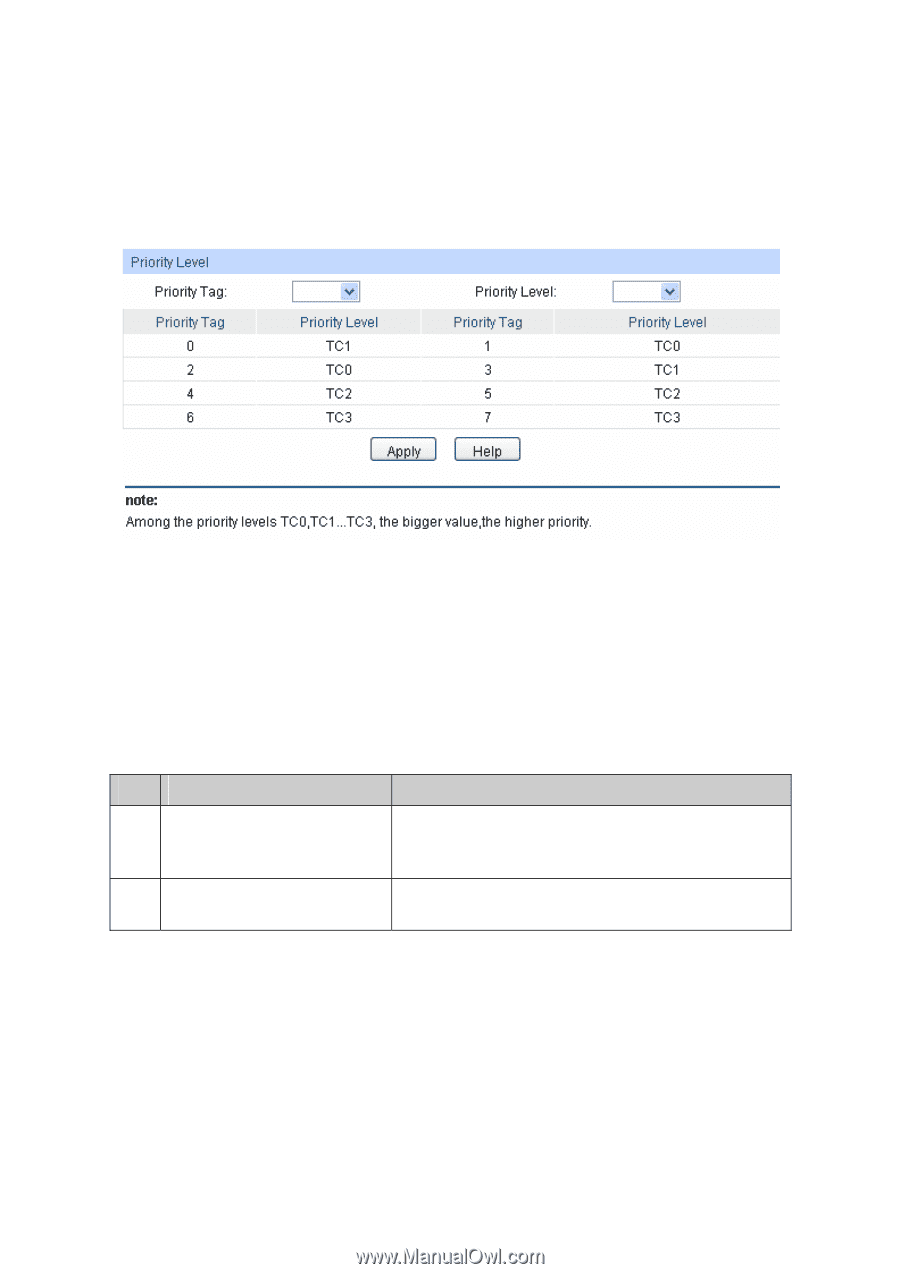
9.1.3 802.1P Priority On this page you can configure 802.1P priority. 802.1P gives the Pri field in 802.1Q tag a recommended definition. This field is used to divide packets into 8 priorities. When 802.1P Priority is enabled, the packets with 802.1Q tag are mapped to different priority levels based on 802.1P priority mode. The untagged packets are mapped based on port priority mode. Choose the menu QoS→DiffServ→802.1P Priority to load the following page. Figure 9-8 802.1P Priority The following entries are displayed on this screen: ¾ Priority Level Priority Tag: Priority Level: Indicates the precedence level defined by IEEE802.1P. Indicates the priority level the packets with tag are mapped to. The priority levels are labeled as TC 0, TC1, TC2 and TC3. Configuration Procedure: Step Operation Description 1 Configure the mapping Required. On QoS→DiffServ→802.1P Priority page, relation between the 802.1P configure the mapping relation between the 802.1P priority and TC priority and TC. 2 Select a schedule mode Required. On QoS→DiffServ→Schedule Mode page,, select a schedule mode. 9.1.4 DSCP Priority On this page you can configure DSCP priority. DSCP (DiffServ Code Point) is a new definition to IP ToS field given by IEEE. This field is used to divide IP datagram into 64 priorities. When DSCP Priority is enabled, IP datagram are mapped to different priority levels based on DSCP priority mode; non-IP datagram with 802.1Q tag are mapped to different priority levels based on 802.1P priority mode if 8021.1P Priority mode is enabled; the untagged non-IP datagram are mapped based on port priority mode. Choose the menu QoS→DiffServ→DSCP Priority to load the following page. 112