TP-Link TL-SG3216 TL-SG3216 V1 User Guide - Page 161
DoS Attack Type, Description, Network Security, DoS Defend
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG3216 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 161 highlights
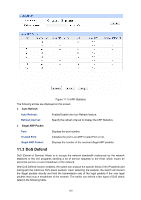
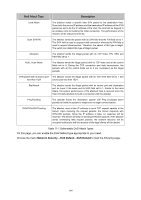
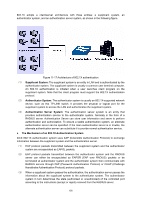
DoS Attack Type Description Land Attack The attacker sends a specific fake SYN packet to the destination Host. Since both the source IP address and the destination IP address of the SYN packet are set to be the IP address of the Host, the Host will be trapped in an endless circle for building the initial connection. The performance of the network will be reduced extremely. Scan SYNFIN The attacker sends the packet with its SYN field and the FIN field set to 1. The SYN field is used to request initial connection whereas the FIN field is used to request disconnection. Therefore, the packet of this type is illegal. The switch can defend this type of illegal packet. Xmascan The attacker sends the illegal packet with its TCP index, FIN, URG and PSH field set to 1. NULL Scan Attack The attacker sends the illegal packet with its TCP index and all the control fields set to 0. During the TCP connection and data transmission, the packets with all the control fields set to 0 are considered as the illegal packets. SYN packet with its source port The attacker sends the illegal packet with its TCP SYN field set to 1 and less than 1024 source port less than 1024. Blat Attack The attacker sends the illegal packet with its source port and destination port on Layer 4 the same and its URG field set to 1. Similar to the Land Attack, the system performance of the attacked Host is reduced since the Host circularly attempts to build a connection with the attacker. Ping Flooding The attacker floods the destination system with Ping broadcast storm packets to forbid the system to respond to the legal communication. SYN/SYN-ACK Flooding The attacker uses a fake IP address to send TCP request packets to the Server. Upon receiving the request packets, the Server responds with SYN-ACK packets. Since the IP address is fake, no response will be returned. The Server will keep on sending SYN-ACK packets. If the attacker sends overflowing fake request packets, the network resource will be occupied maliciously and the requests of the legal clients will be denied. Table 11-1 Defendable DoS Attack Types On this page, you can enable the DoS Defend type appropriate to your need. Choose the menu Network Security→DoS Defend→DoS Defend to load the following page. 154