TP-Link TL-SG3216 TL-SG3216 V1 User Guide - Page 37
Port Mirror
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG3216 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
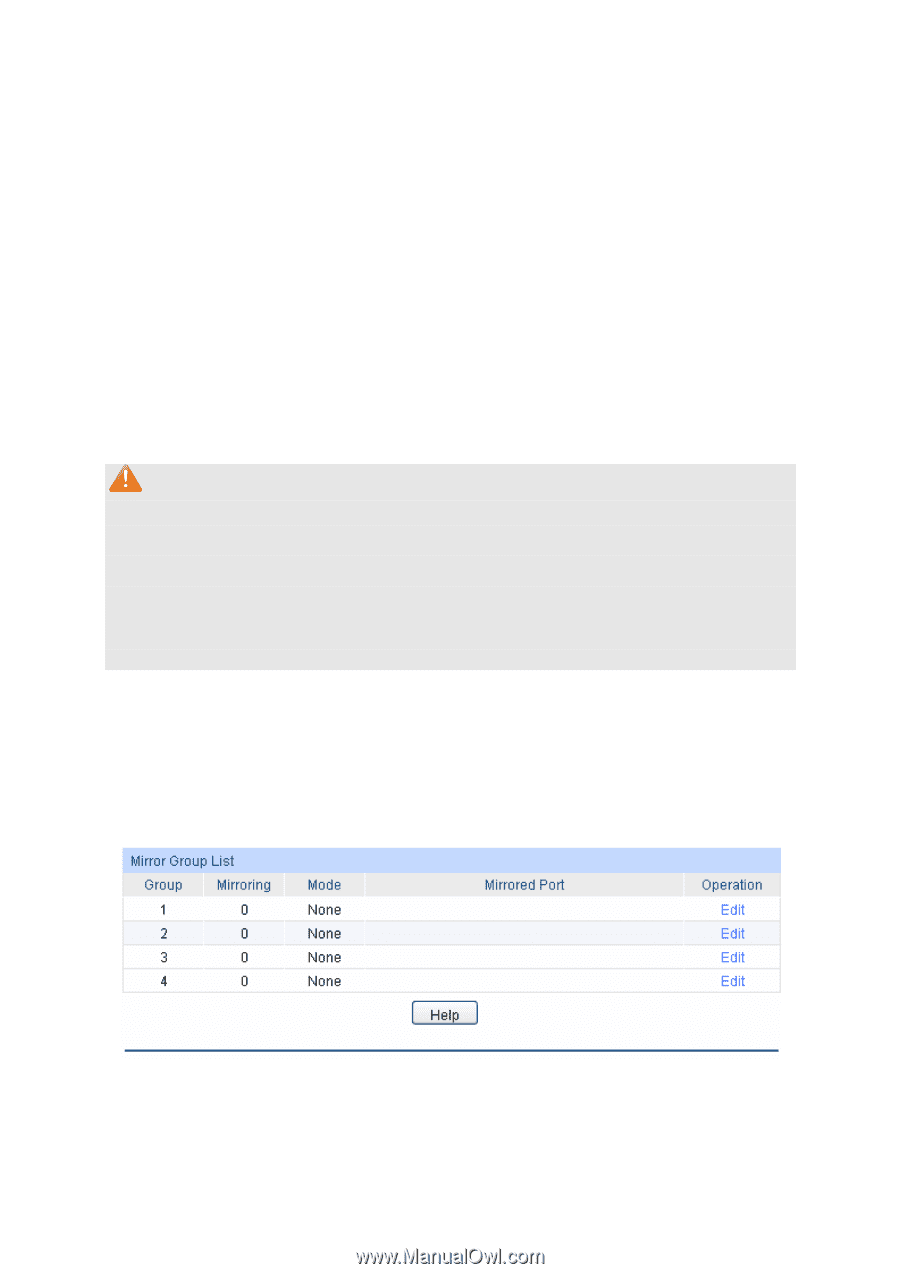
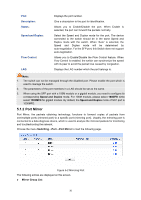
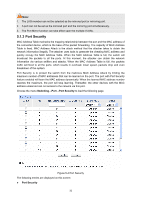
Port: Description: Status: Speed and Duplex: Flow Control: LAG: Displays the port number. Give a description to the port for identification. Allows you to Enable/Disable the port. When Enable is selected, the port can forward the packets normally. Select the Speed and Duplex mode for the port. The device connected to the switch should be in the same Speed and Duplex mode with the switch. When "Auto" is selected, the Speed and Duplex mode will be determined by auto-negotiation. For the SFP port, this Switch does not support auto-negotiation. Allows you to Enable/Disable the Flow Control feature. When Flow Control is enabled, the switch can synchronize the speed with its peer to avoid the packet loss caused by congestion. Displays the LAG number which the port belongs to. Note: 1. The switch can not be managed through the disabled port. Please enable the port which is used to manage the switch. 2. The parameters of the port members in a LAG should be set as the same. 3. When using the SFP port with a 100M module or a gigabit module, you need to configure its corresponding Speed and Duplex mode. For 100M module, please select 100MFD while select 1000MFD for gigabit module. By default, the Speed and Duplex mode of SFP port is 1000MFD. 5.1.2 Port Mirror Port Mirror, the packets obtaining technology, functions to forward copies of packets from one/multiple ports (mirrored port) to a specific port (mirroring port). Usually, the mirroring port is connected to a data diagnose device, which is used to analyze the mirrored packets for monitoring and troubleshooting the network. Choose the menu Switching→Port→Port Mirror to load the following page. Figure 5-2 Mirroring Port The following entries are displayed on this screen. ¾ Mirror Group List 30