TP-Link TL-SG3216 TL-SG3216 V1 User Guide - Page 164
X Authentication Procedure
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG3216 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 164 highlights
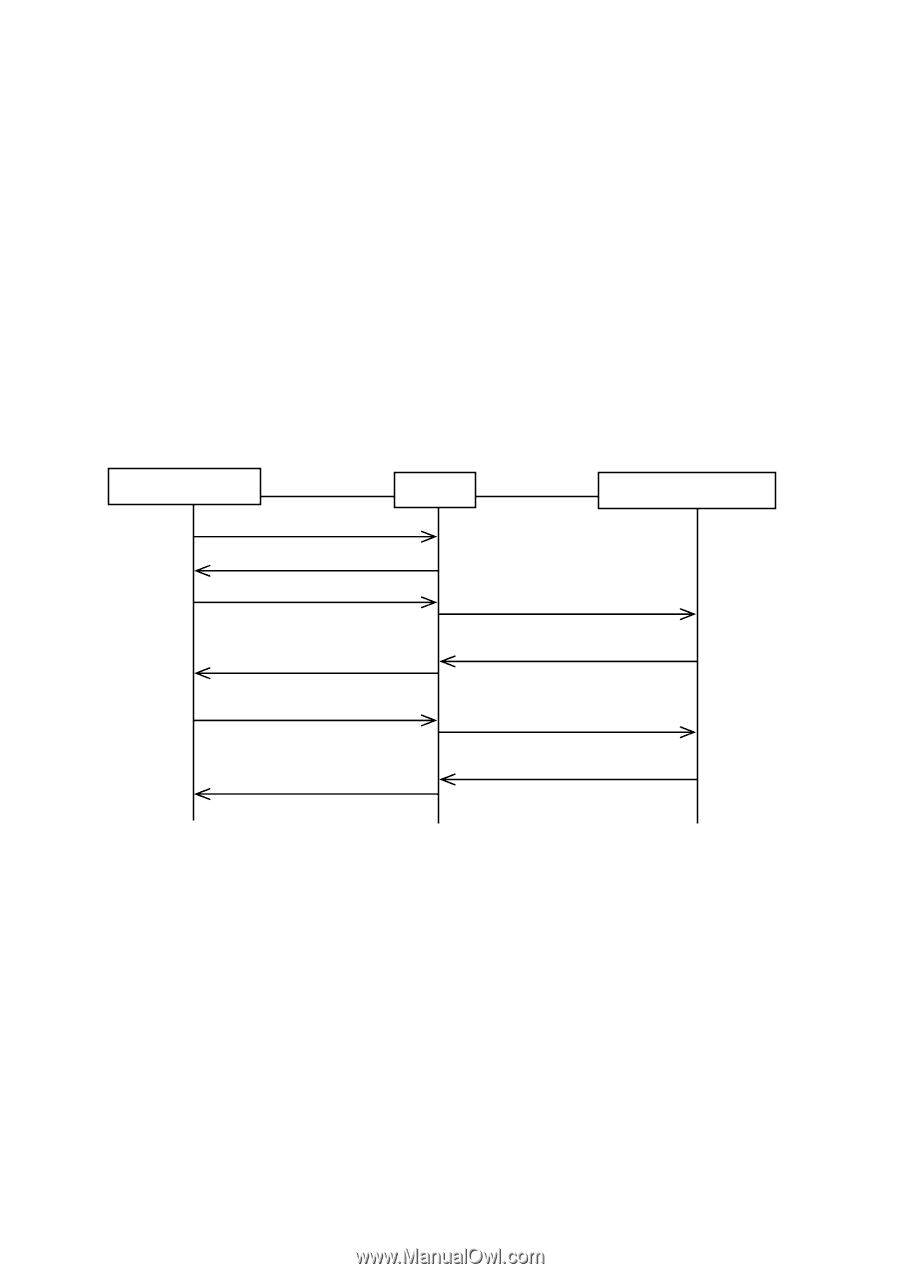
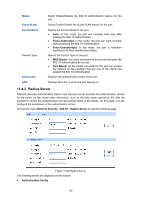
¾ 802.1X Authentication Procedure An 802.1X authentication can be initiated by supplicant system or authenticator system. When the authenticator system detects an unauthenticated supplicant in LAN, it will initiate the 802.1X authentication by sending EAP-Request/Identity packets to the supplicant. The supplicant system can also launch an 802.1X client program to initiate an 802.1X authentication through the sending of an EAPOL-Start packet to the switch, This TP-LINK switch can authenticate supplicant systems in EAP relay mode or EAP terminating mode. The following illustration of these two modes will take the 802.1X authentication procedure initiated by the supplicant system for example. (1) EAP Relay Mode This mode is defined in 802.1X. In this mode, EAP-packets are encapsulated in higher level protocol (such as EAPOR) packets to allow them successfully reach the authentication server. This mode normally requires the RADIUS server to support the two fields of EAP: the EAP-message field and the Message-authenticator field. This switch supports EAP-MD5 authentication way for the EAP relay mode. The following figure describes the basic EAP-MD5 authentication procedure. Supplicant System EAP Switch EAP Authentication Server EAPOL-Start EAP-Request/Identity EAP-Response/Identity RADIUS-Access-Request EAP-Request RADIUS-Access-Challenge EAP-Response RADIUS-Access-Request EAP-Success RADIUS-Access-Accept Figure 11-18 EAP-MD5 Authentication Procedure 1. A supplicant system launches an 802.1X client program via its registered user name and password to initiate an access request through the sending of an EAPOL-Start packet to the switch. The 802.1X client program then forwards the packet to the switch to start the authentication process. 2. Upon receiving the authentication request packet, the switch sends an EAP-Request/Identity packet to ask the 802.1X client program for the user name. 3. The 802.1X client program responds by sending an EAP-Response/Identity packet to the switch with the user name included. The switch then encapsulates the packet in a RADIUS Access-Request packet and forwards it to the RADIUS server. 4. Upon receiving the user name from the switch, the RADIUS server retrieves the user name, finds the corresponding password by matching the user name in its database, encrypts the password using a randomly-generated key, and sends the key to the switch through an RADIUS Access-Challenge packet. The switch then sends the key to the 802.1X client program. 157