TP-Link TL-SG3216 TL-SG3216 V1 User Guide - Page 147
DHCP Snooping
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG3216 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 147 highlights
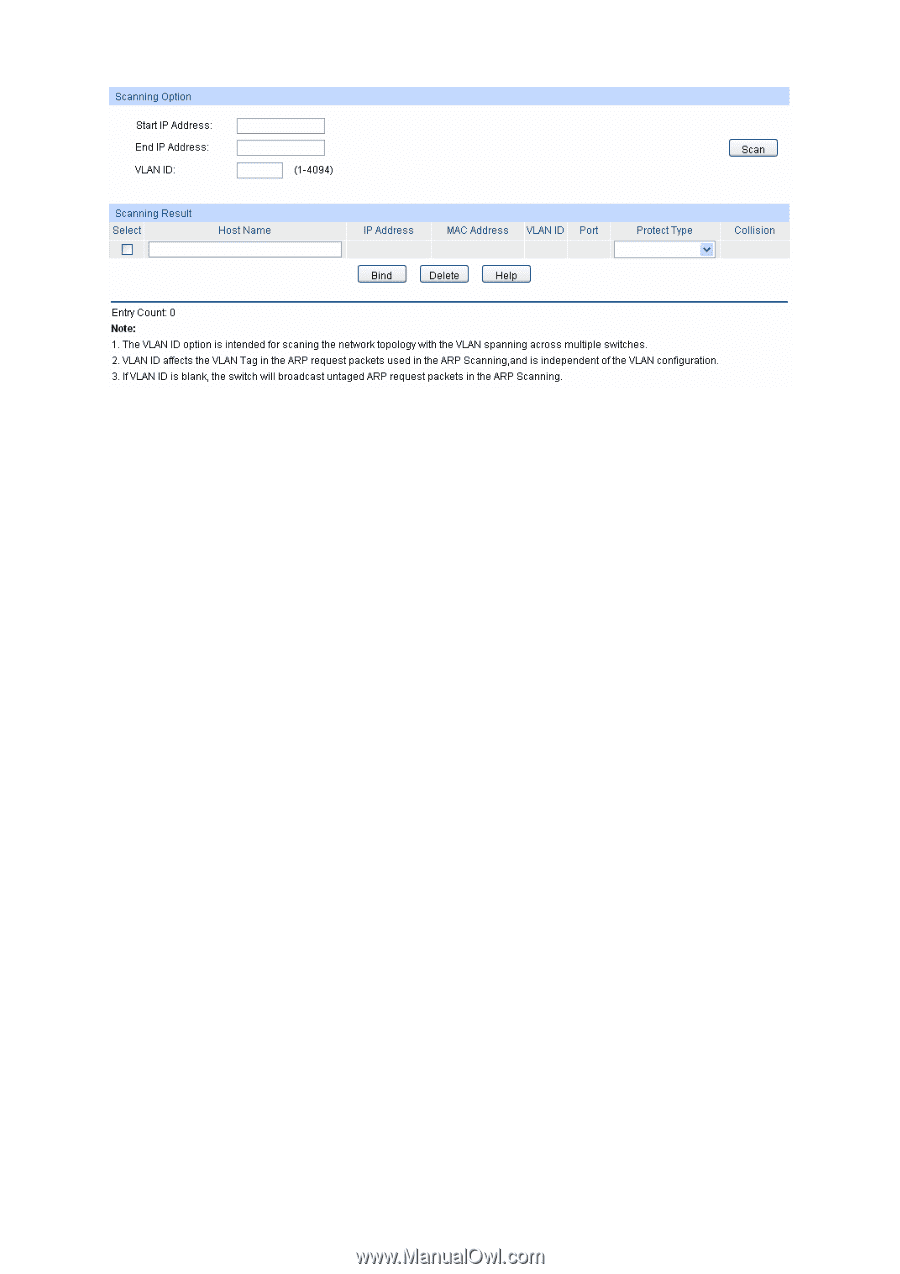
Figure 11-4 ARP Scanning The following entries are displayed on this screen: ¾ Scanning Option Start IP Address: End IP Address: VLAN ID: Scan: Specify the Start IP Address. Specify the End IP Address. Enter the VLAN ID. If blank, the switch will send the untagged packets for scanning. Click the Scan button to scan the Hosts in the LAN. ¾ Scanning Result Select: Host Name: IP Address: MAC Address: VLAN ID: Port: Protect Type: Collision: Select the desired entry to be bound or deleted. Displays the Host Name here. Displays the IP Address of the Host. Displays the MAC Address of the Host. Displays the VLAN ID here. Displays the number of port connected to the Host. Displays the Protect Type of the entry. Displays the Collision status of the entry. • Warning: Indicates that the collision may be caused by the MSTP function. • Critical: Indicates that the entry has a collision with the other entries. 11.1.4 DHCP Snooping Nowadays, the network is getting larger and more complicated. The amount of the PCs always exceeds that of the assigned IP addresses. The wireless network and the laptops are widely used and the locations of the PCs are always changed. Therefore, the corresponding IP address of the PC should be updated with a few configurations. DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, the 140