TP-Link TL-SG3216 TL-SG3216 V1 User Guide - Page 63
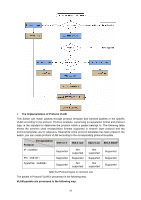
Protocol VLAN
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG3216 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
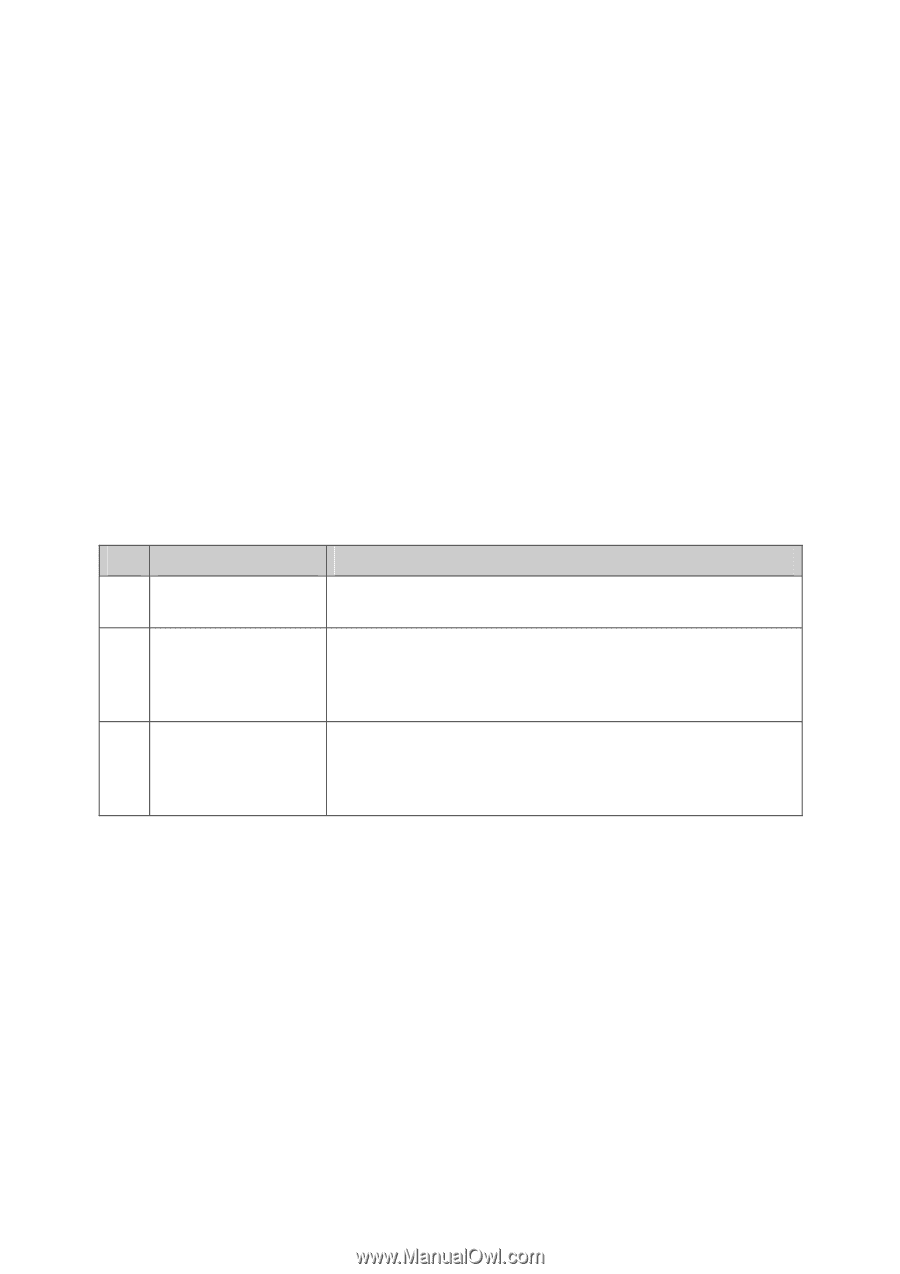
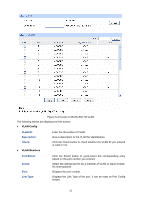
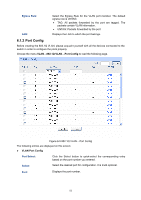
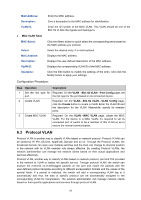
MAC Address: Description: VLAN ID: ¾ MAC VLAN Table MAC Select: Select: MAC Address: Description: VLAN ID: Operation: Enter the MAC address. Give a description to the MAC address for identification. Enter the ID number of the MAC VLAN. This VLAN should be one of the 802.1Q VLANs the ingress port belongs to. Click the Select button to quick-select the corresponding entry based on the MAC address you entered. Select the desired entry. It is multi-optional. Displays the MAC address. Displays the user-defined description of the MAC address. Displays the corresponding VLAN ID of the MAC address. Click the Edit button to modify the settings of the entry. And click the Modify button to apply your settings. Configuration Procedure: Step Operation Description 1 Set the link type for Required. On the VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→Port Config page, set port. the link type for the port based on its connected device. 2 Create VLAN. Required. On the VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→VLAN Config page, click the Create button to create a VLAN. Enter the VLAN ID and the description for the VLAN. Meanwhile, specify its member ports. 3 Create MAC VLAN. Required. On the VLAN→MAC VLAN page, create the MAC VLAN. For the device in a MAC VLAN, it's required to set its connected port of switch to be a member of this VLAN so as to ensure the normal communication. 6.3 Protocol VLAN Protocol VLAN is another way to classify VLANs based on network protocol. Protocol VLANs can be sorted by IP, IPX, DECnet, AppleTalk, Banyan and so on. Through the Protocol VLANs, the broadcast domain can span over multiple switches and the Host can change its physical position in the network with its VLAN member role always effective. By creating Protocol VLANs, the network administrator can manage the network clients based on their actual applications and services effectively. Protocol VLAN, another way to classify VLANs based on network protocol, can bind ToS provided in the network to VLAN to realize the specific service. Through protocol VLAN, the switch can analyze the received un-VLAN-tagged packets on the port and match the packets with the user-defined protocol template according to different encapsulation formats and the values of the special fields. If a packet is matched, the switch will add a corresponding VLAN tag to it automatically and thus the data of specific protocol can be automatically assigned to the corresponding VLAN for transmission. The network administrator can manage network clients based on their specific applications and services through protocol VLAN. 56