Netgear GSM7248v1 GSM7224 Administration manual - Page 122
Understanding Switch Stacks, switch stack, stack master, stack members, stack member number
 |
View all Netgear GSM7248v1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 122 highlights
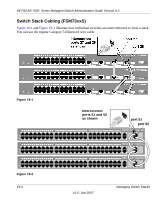
NETGEAR 7000 Series Managed Switch Administration Guide Version 6.0 Understanding Switch Stacks A switch stack is a set of up to eight Ethernet switches connected through their stacking ports. One of the switches controls the operation of the stack and is called the stack master. The stack master and the other switches in the stack are stack members. The stack members use stacking technology to behave and work together as a unified system. Layer 2 and Layer 3 protocols present the entire switch stack as a single entity to the network. The stack master is the single point of stack-wide management. From the stack master, you configure: • System-level (global) features that apply to all stack members • Interface-level features for all interfaces on any stack member A switch stack is identified in the network by its network IP address. The network IP address is assigned according to the MAC address of the stack master. Every stack member is uniquely identified by its own stack member number. All stack members are eligible stack masters. If the stack master becomes unavailable, the remaining stack members participate in electing a new stack master from among themselves. A set of factors determine which switch is elected the stack master. These factors are: 1. The switch that is master always has priority to retain the role of master 2. Assigned priority 3. MAC address If the master cannot be selected by (1), then (2) is used. If (2) does not resolve which stack member becomes stack master, then (3) is used. The stack master contains the saved and running configuration files for the switch stack. The configuration files include the system-level settings for the switch stack and the interface-level settings for all stack members. Each stack member retains a copy of the saved file for backup purposes. If the master is removed from the stack, another member will be elected master, and will then run from that saved configuration. You can use these methods to manage switch stacks: • Stack web interface • Command line interface (CLI) over a serial connection to the console port of the master • A network management application through the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) 19-2 v1.0, Jan 2007 Managing Switch Stacks