Netgear GSM7248v1 GSM7224 Administration manual - Page 83
Class of Service (CoS) Queuing, Overview, CoS Queue Mapping, Trusted Ports
 |
View all Netgear GSM7248v1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 83 highlights
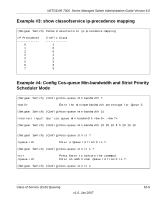
Chapter 10 Class of Service (CoS) Queuing This section describes the Class of Service (CoS) Queue Mapping and Traffic Shaping features. Overview Each port has one or more queues for packet transmission. During configuration, you can determine the mapping and configuration of these queues. Based on service rate and other criteria you configure, queues provide preference to specified packets. If a delay becomes necessary, the system holds packets until the scheduler authorizes transmission. As queues become full, packets are dropped. Packet drop precedence indicates the packet's sensitivity to being dropped during times of queue congestion. CoS mapping, queue parameters, and queue management are configurable per interface. Queue management is configurable per interface. Some hardware implementations allow queue depth management using tail dropping or Weighted random early discard (WRED). Some hardware implementations allow queue depth management using tail dropping. The operation of CoS Queuing involves queue mapping and queue configuration. CoS Queue Mapping CoS Queue Mapping uses trusted and untrusted ports. Trusted Ports • System takes at face value certain priority designation for arriving packets. • Trust applies only to packets that have that trust information. • Can only have one trust field at a time - per port. - 802.1p User Priority (default trust mode - Managed through Switching configuration) v1.0, Jan 2007 10-1