Netgear GSM7248v1 GSM7224 Administration manual - Page 84
Untrusted Ports, CoS Queue Configuration
 |
View all Netgear GSM7248v1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 84 highlights
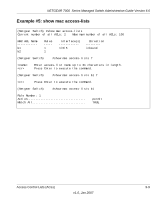
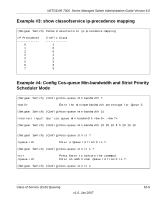
NETGEAR 7000 Series Managed Switch Administration Guide Version 6.0 - IP Precedence - IP DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) The system can assign service level based upon the 802.1p priority field of the L2 header. You configure this by mapping the 802.1p priorities to one of three traffic class queues. These queues are: • Queue 2 - Minimum of 50% of available bandwidth • Queue 1 - Minimum of 33% of available bandwidth • Queue 0 - Lowest priority, minimum of 17% of available bandwidth For untagged traffic, you can specify default 802.1p priority on a per-port basis. Untrusted Ports • No incoming packet priority designation is trusted, therefore the port default priority value is used. • All ingress packets from Untrusted ports, where the packet is classified by an ACL or a DiffServ policy, are directed to specific CoS queues on the appropriate egress port. That specific CoS queue is determined by either the default priority of the port or a DiffServ or ACL assign queue attribute. • Used when trusted port mapping is unable to be honored - i.e. when a non-IP DSCP packet arrives at a port configured to trust IP DSCP. CoS Queue Configuration CoS queue configuration involves port egress queue configuration and drop precedence configuration (per queue). The design of these on a per queue, per drop precedence basis allows the user to create the desired service characteristics for different types of traffic. Port Egress Queue Configuration • Scheduler Type - Strict vs. Weighted • Minimum guaranteed bandwidth • Maximum allowed bandwidth - Per queue shaping • Queue management type 10-2 v1.0, Jan 2007 Class of Service (CoS) Queuing