ZyXEL ZYWALL USG 100 User Guide - Page 45
Protecting Your Network, 3.1 Firewall, Firewall - nat configuration
 |
View all ZyXEL ZYWALL USG 100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 45 highlights
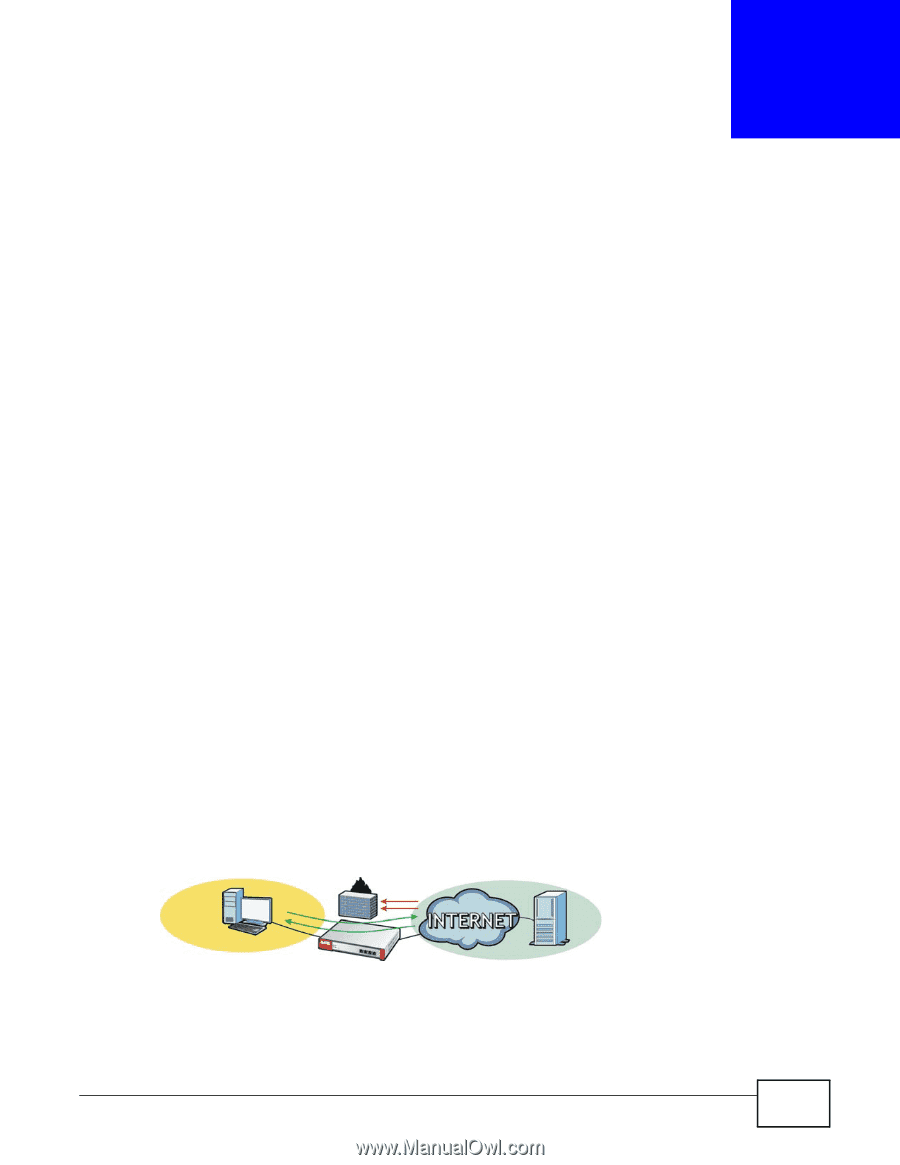
CHAPTER 3 Protecting Your Network These sections cover configuring the ZyWALL to protect your network. • Firewall on page 45 • User-aware Access Control on page 46 • Endpoint Security (EPS) on page 47 • Device and Service Registration on page 47 • Anti-Virus Policy Configuration on page 48 • IDP Profile Configuration on page 50 • ADP Profile Configuration on page 51 • Content Filter Profile Configuration on page 54 • Viewing Content Filter Reports on page 56 • Anti-Spam Policy Configuration on page 60 3.1 Firewall The firewall controls the travel of traffic between or within zones for services using static port numbers. Use application patrol to control services using flexible/dynamic port numbers (see Section 5.7 on page 113 for an example). The firewall can also control traffic for NAT (DNAT) and policy routes (SNAT). Firewall rules can use schedule, user, user groups, address, address group, service, and service group objects. To-ZyWALL firewall rules control access to the ZyWALL itself including management access. By default the firewall allows various types of management from the LAN, HTTPS from the WAN and no management from the DMZ. The firewall also limits the number of user sessions. This example shows the ZyWALL's default firewall behavior for WAN to LAN traffic and how stateful inspection works. A LAN user can initiate a Telnet session from within the LAN zone and the firewall allows the response. However, the firewall blocks Telnet traffic initiated from the WAN zone and destined for the LAN zone. The firewall allows VPN traffic between any of the networks. Figure 26 Default Firewall Action LAN WAN ZyWALL USG100-PLUS User's Guide 45