ZyXEL ZYWALL USG 100 User Guide - Page 93
Managing Traffic, 5.1 How to Con Bandwidth Management
 |
View all ZyXEL ZYWALL USG 100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 93 highlights
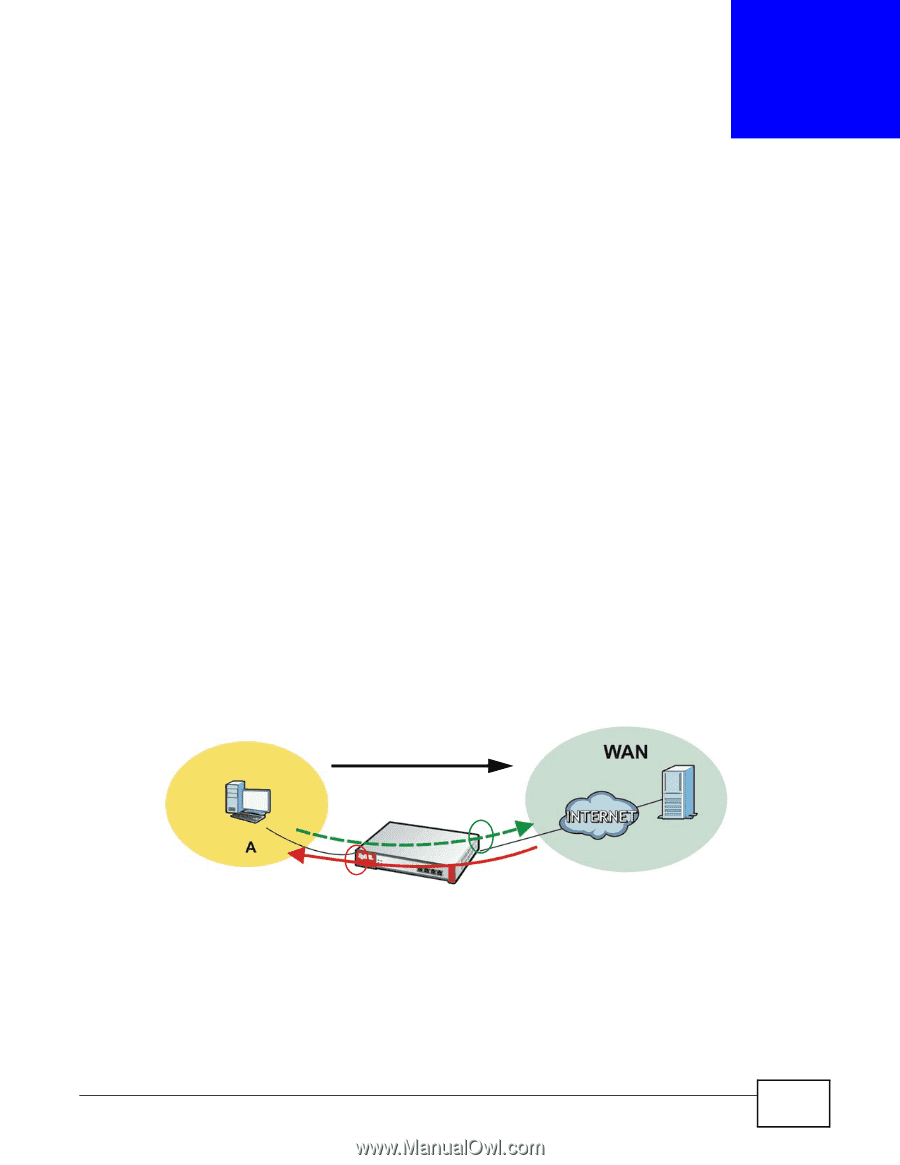
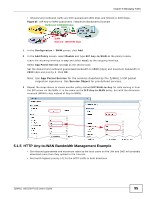
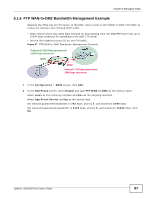
CHAPTER 5 Managing Traffic These sections cover controlling the traffic going through the ZyWALL. • How to Configure Bandwidth Management on page 93 • How to Configure a Trunk for WAN Load Balancing • How to Use Multiple Static Public WAN IP Addresses for LAN-to-WAN Traffic on page 103 • How to Configure DNS Inbound Load Balancing on page 104 • How to Allow Public Access to a Web Server on page 106 • How to Manage Voice Traffic on page 108 • How to Limit Web Surfing and MSN to Specific People on page 113 5.1 How to Configure Bandwidth Management Bandwidth management is very useful when applications are competing for limited bandwidth. Connection and Packet Directions Bandwidth management looks at the connection's direction from the interface it was initiated on to the interface it goes out. The connection initiator sends outbound traffic and receives inbound traffic. The ZyWALL controls each flow's bandwidth as it goes out through an interface or VPN tunnel. For example, a LAN1 to WAN connection is initiated from LAN1 and goes to the WAN. Figure 34 LAN1 to WAN Connection and Packet Directions LAN1 Connection Outbound BWM BWM Inbound • Outbound traffic goes from a LAN1 device to the WAN. The ZyWALL applies bandwidth management before sending the packets out a WAN interface. • Inbound traffic comes back from the WAN to the LAN1 device. The ZyWALL applies bandwidth management before sending the traffic out a LAN1 interface. You can set outbound and inbound guaranteed and maximum bandwidths for an application. ZyWALL USG100-PLUS User's Guide 93