ZyXEL ZYWALL USG 100 User Guide - Page 94
Bandwidth Allocation Example, 5.1.2 Setting the Interface’s Bandwidth - bandwidth management
 |
View all ZyXEL ZYWALL USG 100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 94 highlights
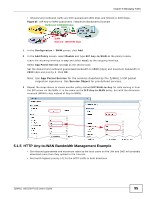
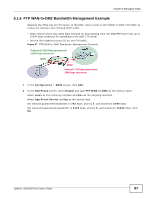
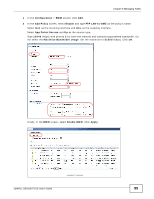
Chapter 5 Managing Traffic 5.1.1 Bandwidth Allocation Example Say a 10-person office has WAN1 connected to a 50 Mbps downstream and 5 Mbps upstream VDSL line and you want to allocate bandwidth for the following: • SIP: Up to 10 simultaneous 100 Kbps calls guaranteed • Video conferencing: Up to 10 simultaneous 128 Kbps Skype video calls guaranteed • Video streaming: up to 10 simultaneous 256 Kbps sessions • HTTP: Internet access including downloading files for 10 users • SMTP: 10 users sending email • POP3: 10 users receiving email • FTP: 10 users uploading and downloading files Here is an example of allocating the any to WAN connection's inbound and outbound packet flows. Enable Maximize Bandwidth Usage (Max B.U.) on a packet flow to set no limit on it and let it use any available bandwidth on the out-going interface. Table 9 50 Mbps / 5 Mbps Connection Any to WAN Bandwidth Allocation Example GUARANTEED K / MAXIMUM K OR MAX B.U. PRIORITY AND APPLICATION INBOUND OUTBOUND 1 SIP 1000/2000 1000/2000 2 Video conferencing 1280/3840 1280/3840 3 Video streaming 2560/3584 * 4 HTTP 10240/46080 * 4 SMTP * 2048/Max B.U. 4 POP3 10240/Max B.U. * 5 FTP 10240/46080 792/3072 Total guaranteed bandwidth: 35560 Kbps 5120 Kbps * This application does not usually generate enough traffic in this direction to require management. 5.1.2 Setting the Interface's Bandwidth Use the Configuration > Interface screens to set the WAN1 interface's upstream (egress) bandwidth to be equal to (or slightly less than) what the connected device can support. This example uses 5120 Kbps. 5.1.3 SIP Bandwidth Management The most effective way to ensure the quality of SIP calls is to go to the Configuration > BWM screen and enable BWM and select Enable Highest Bandwidth Priority for SIP Traffic. See the following section if you prefer to configure specific bandwidth management rules for SIP instead. 5.1.4 SIP Any-to-WAN and WAN-to-Any Bandwidth Management Example • Manage SIP traffic going to WAN1 from users on the LAN or DMZ. 94 ZyWALL USG100-PLUS User's Guide